








Introduction
What is Radiology?
Further Explanation:
The name implies 'radiation', and many of the types of studies radiologists perform and interpret DO involve radiation, but not all. Historically, the specialty arose after Roentgen discovered x-rays, in 1895. He initially called them "X" rays (for unknown rays), but later objected to this terminology, although the name remained. Some later advocated calling them "roentgen-rays", and one of the international radiology organizations is still called the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS).
Introduction
Subspecialties of Radiology
Question 1:
What are some subspecialties within Radiology?
Thoracic and Cardiovascular Imaging; Abdominal and GI/GU Imaging; Neruroradiology and Head and Neck Imaging; Breast Imaging; Nuclear Medicine; Ultrasound; Interventional Radiology; Emergency Radiology; Musculoskeletal Radiology; Pediatric Radiology;
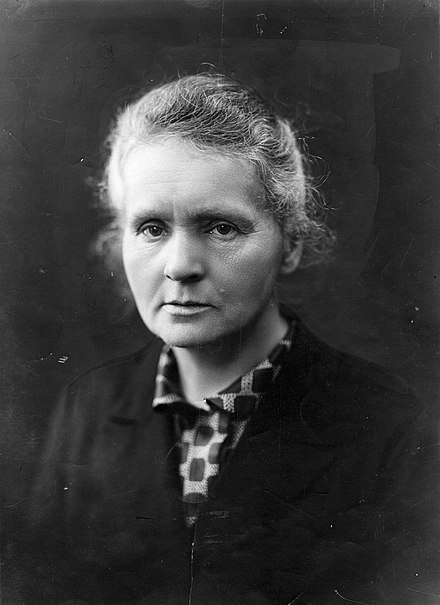
Initially, Radiology included both 'diagnostic' radiology (using various methods to obtain images of the body, for diagnosis of disease), and 'therapeutic' radiology (now called Radiation Oncology--using radiation to treat disease in the body, usually tumors). Marie Curie did some of the first work on use of radium to treat tumors. But in the late 1960's, Radiation Therapy/Radiation Oncology became a separate specialty from the rest of Radiology.

Introduction
Day in the Life
Further Explanation:
One of the perceived advantages of Radiology as a career is that in many settings, the work day can be well defined, without off-hours (call) or unexpected duties away from work. However, this varies considerably depending on what type of Radiology one is practicing. In Breast Imaging, there are generally no call responsibilities and the workday is well-defined. In Interventional Radiology, there is often a heavy call schedule and many times the workday is determined by what cases need attention. Each practice setting is different. Some involve more patient contact (Pediatric Radiology, Interventional Radiology, Breast Radiology), while others may involve less patient contact except when performing procedures (Musculoskeletal Radiology, Abdominal/GI/GU Radiology, Chest/Cardiovascular Radiology).