








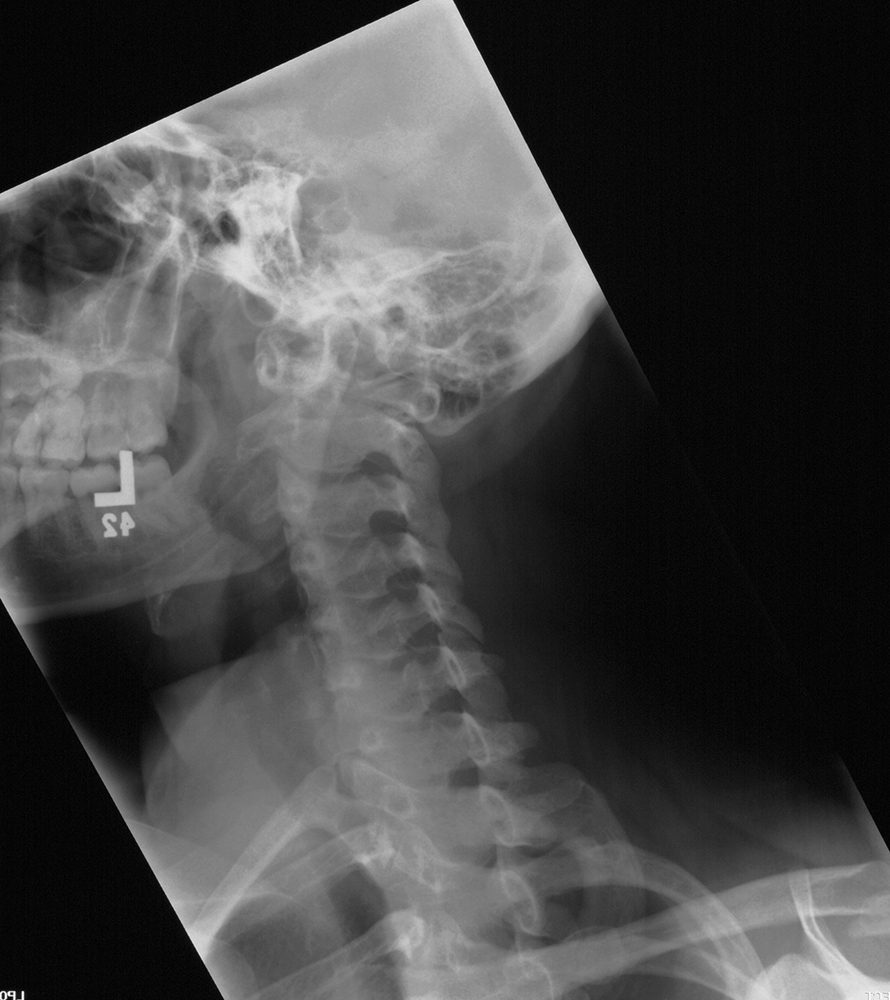
Case 3
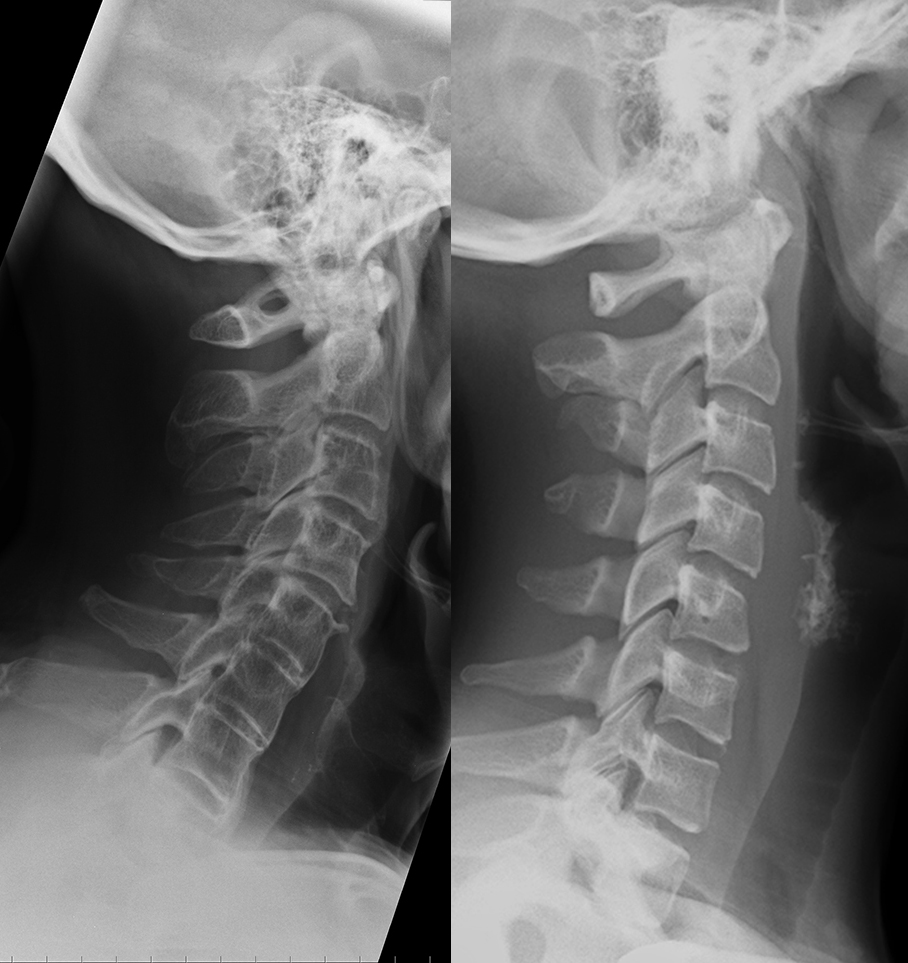
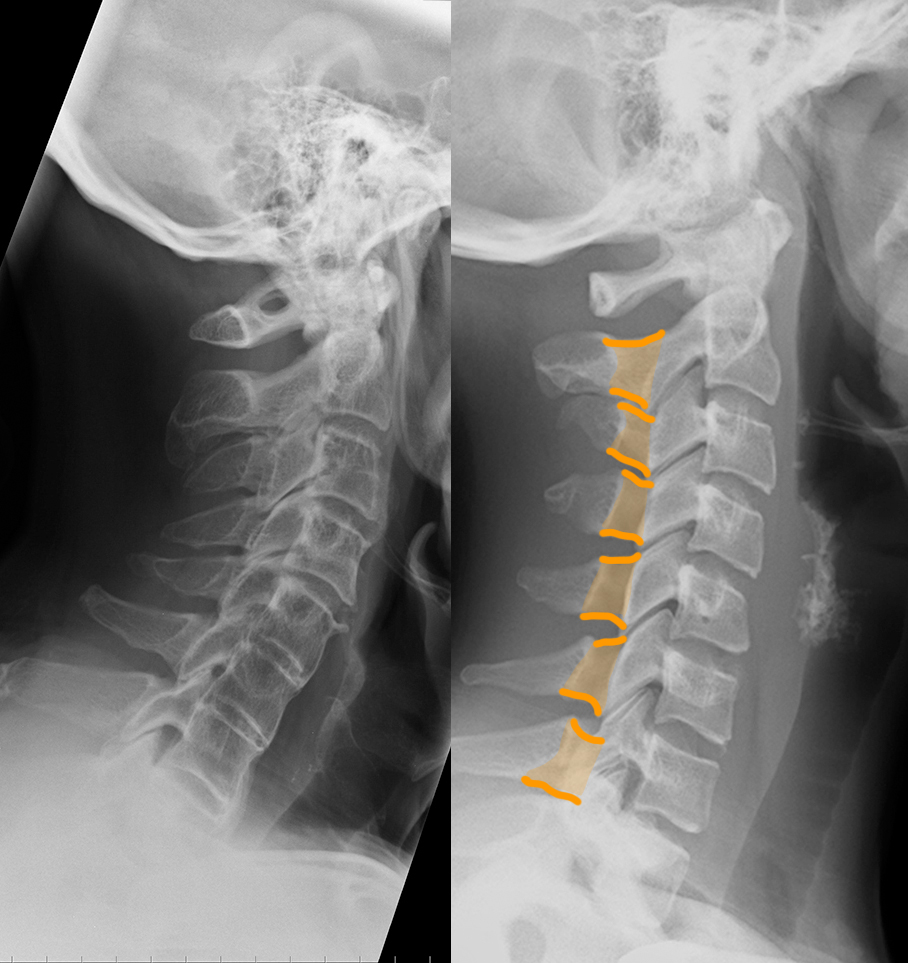
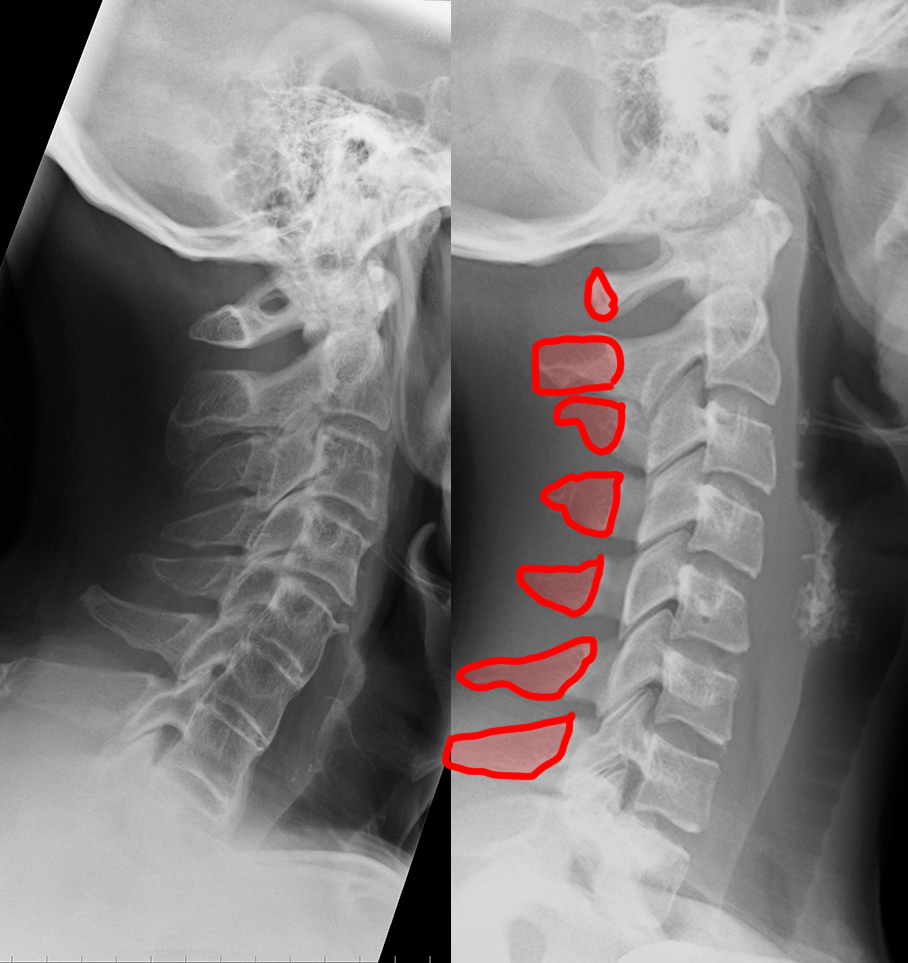
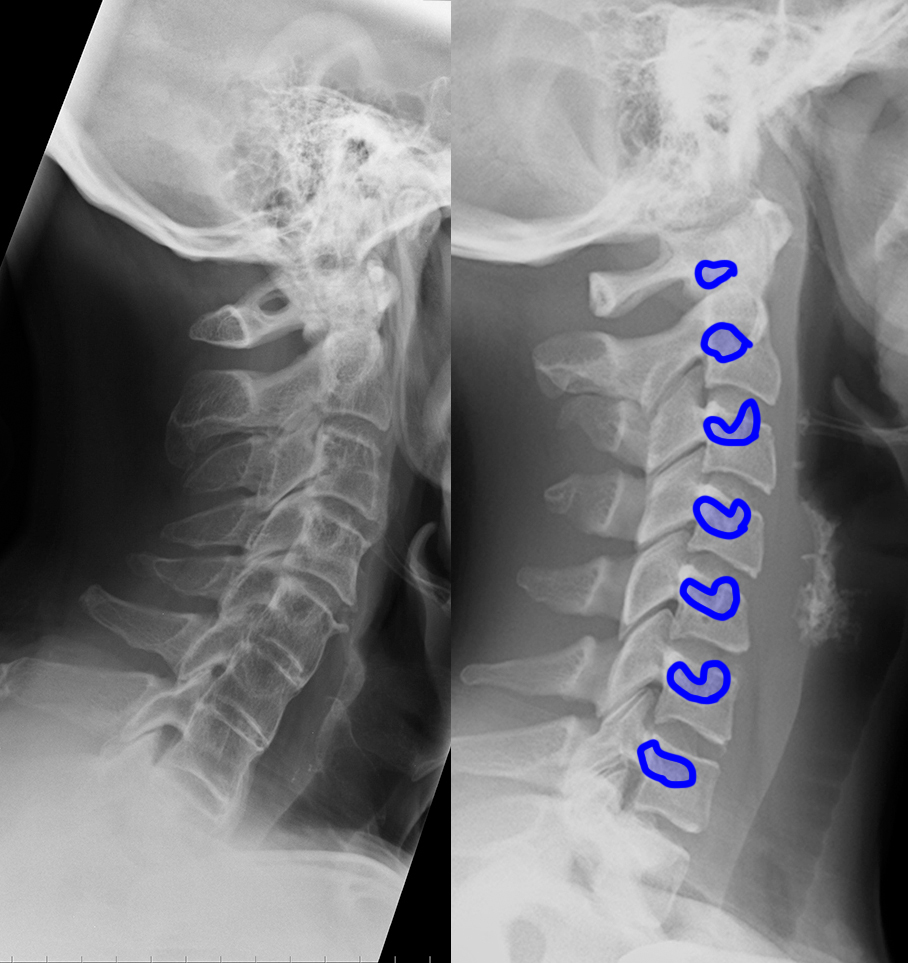
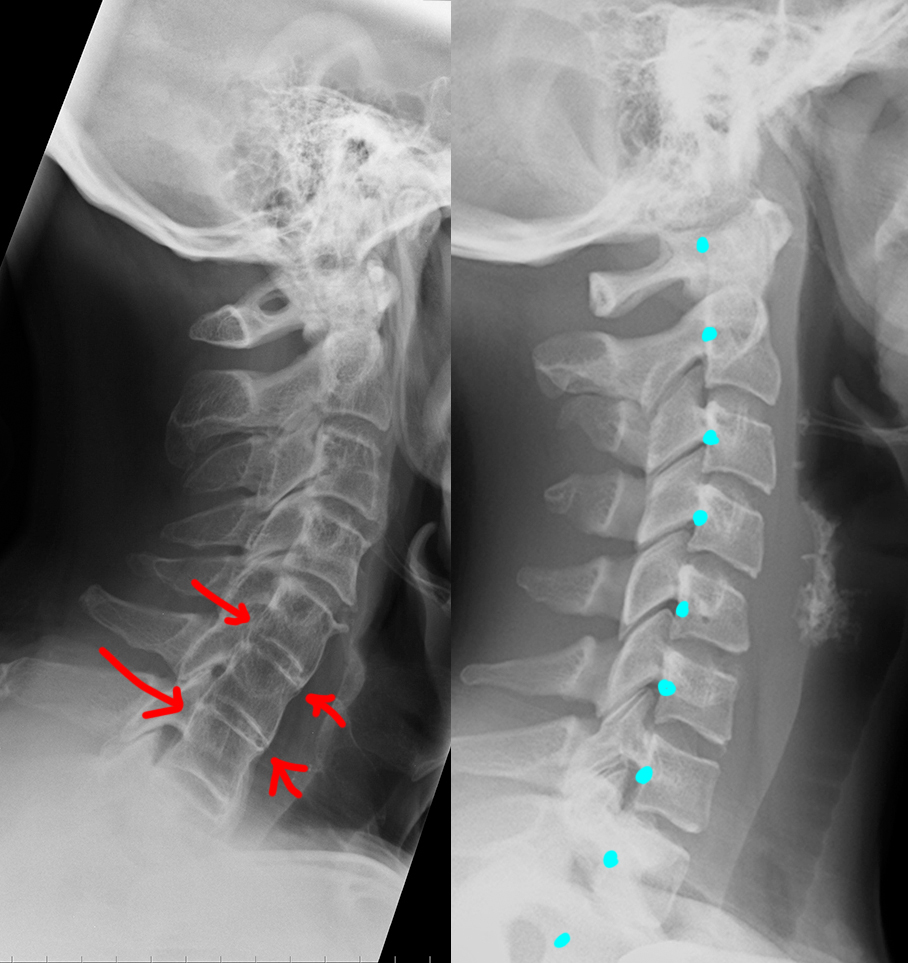
Neck pain after motor vehicle collision. Unrestrained passenger. Patient image is shown to the left and a normal comparison on the right. Try to identify differences between the two.
Question 1:
a) What are these views called?
These are lateral cervical spine radiographs.
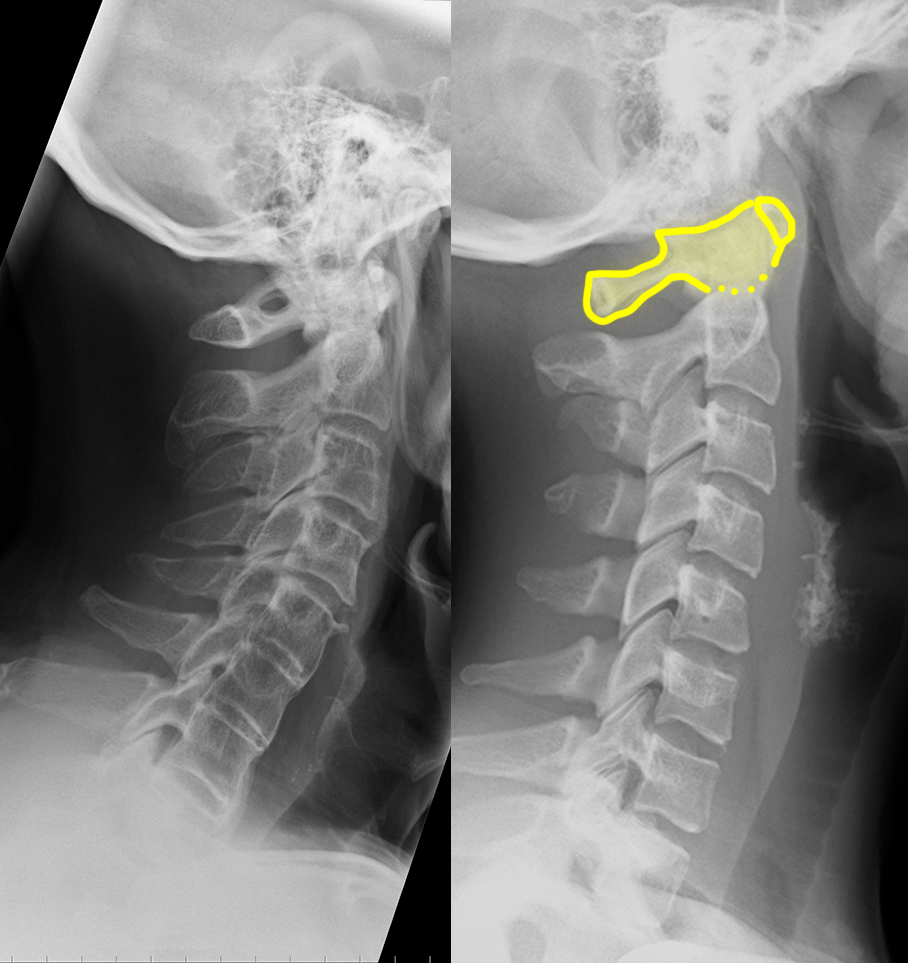
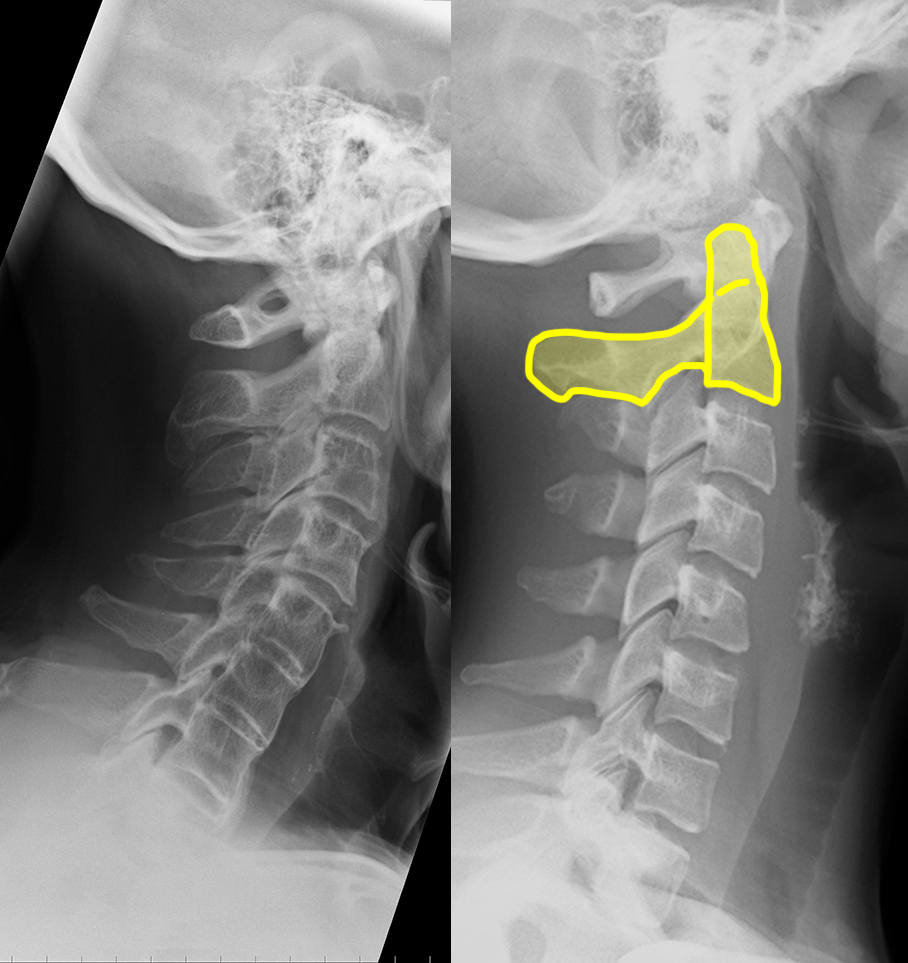
b) Identify the labeled structures on the normal image.
1-C1 (atlas); 2-C2 (axis, including dens/odontoid); 3-C3 vertebra 4-superior articular processes (facets); 5-inferior articular processes (facets) 6-pedicles; 7-laminae; 8-spinous processes; 9-transverse processes
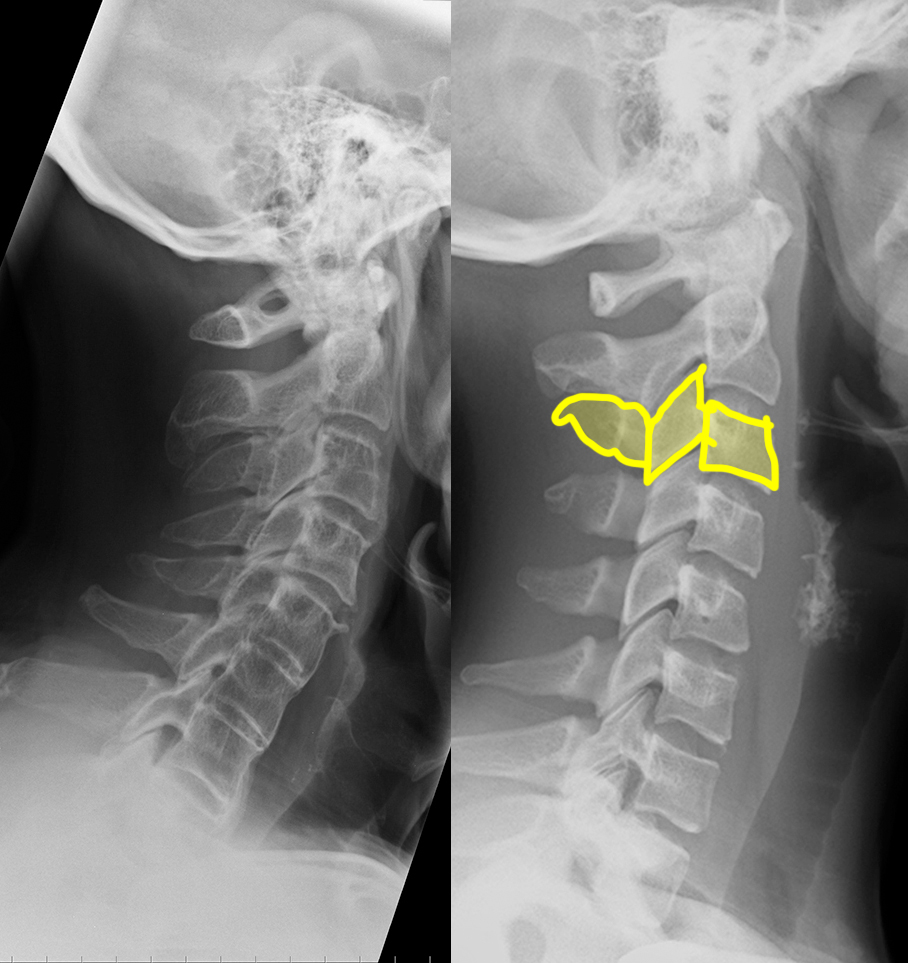
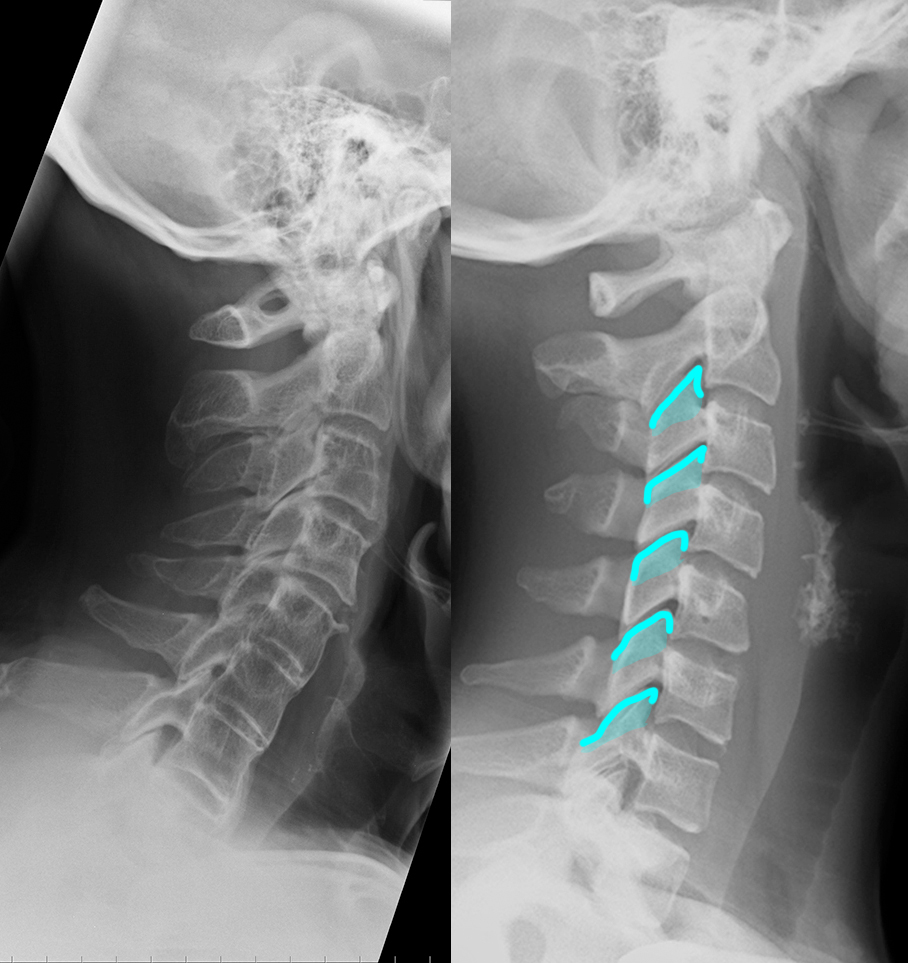
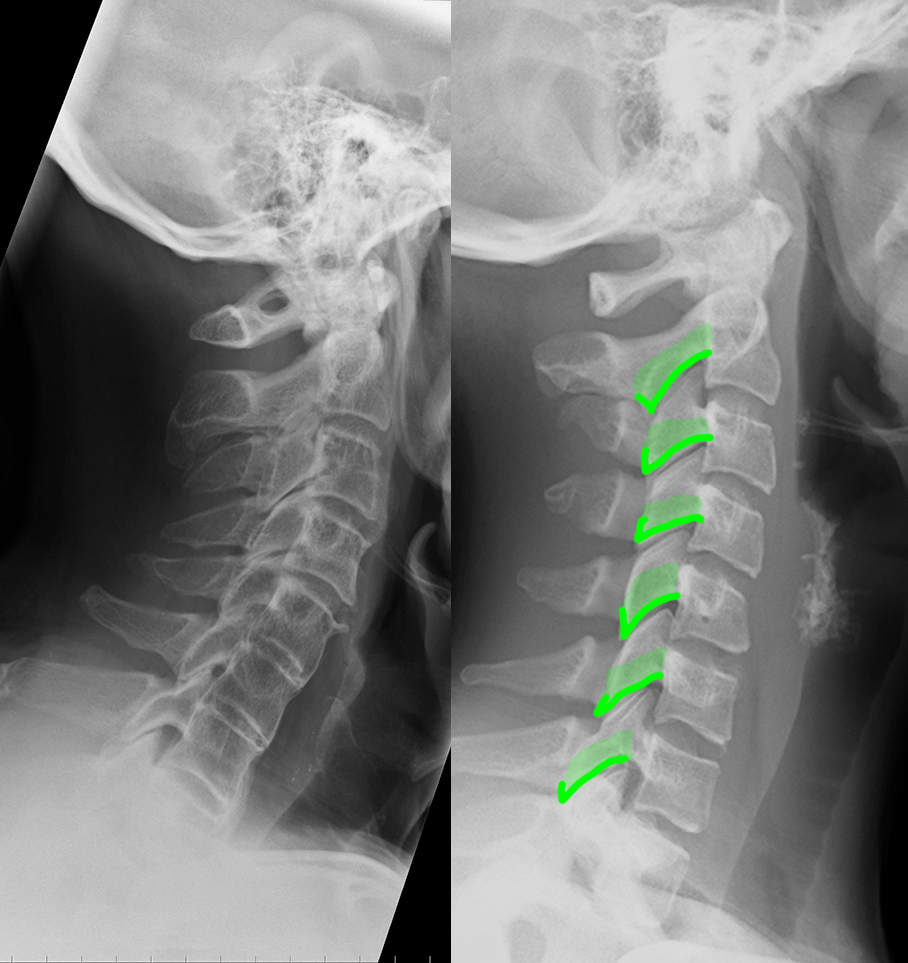
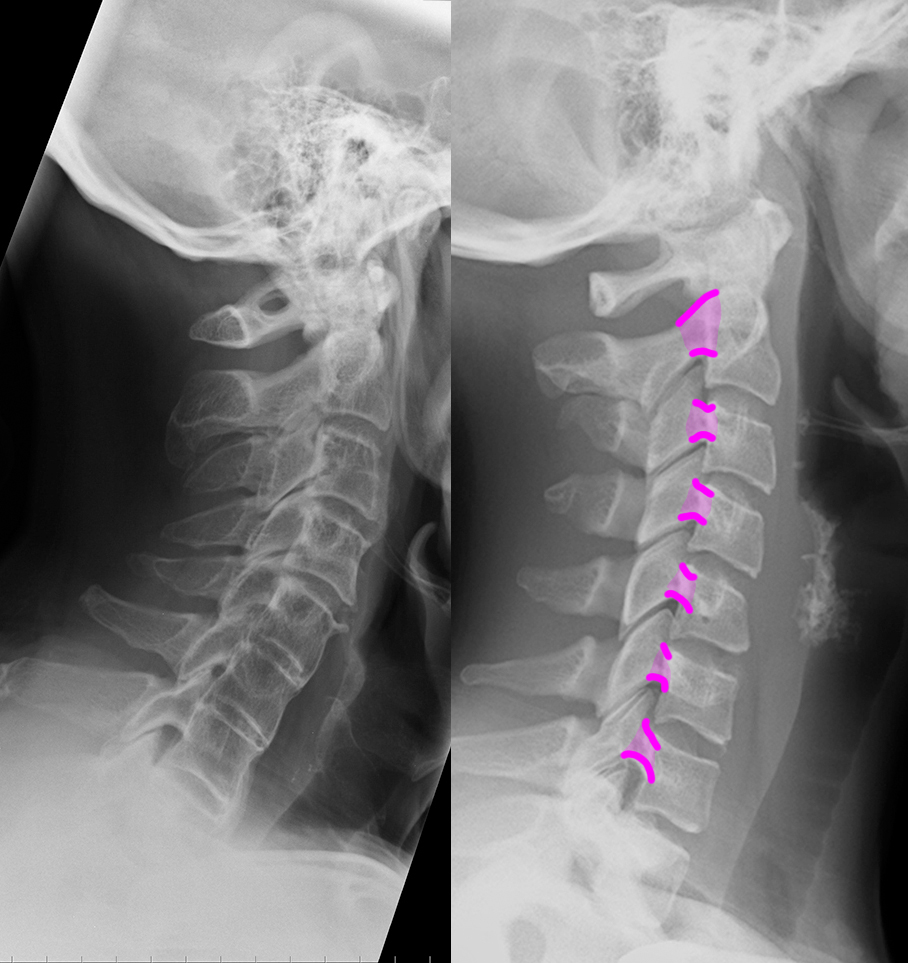
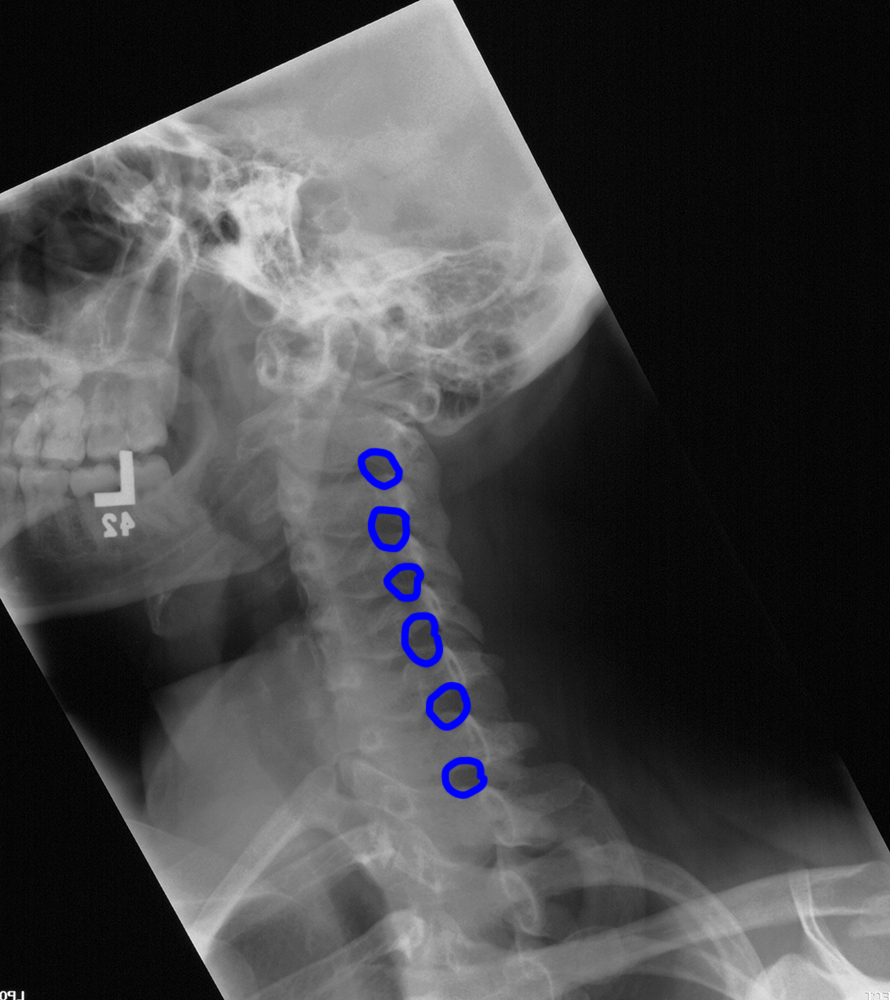
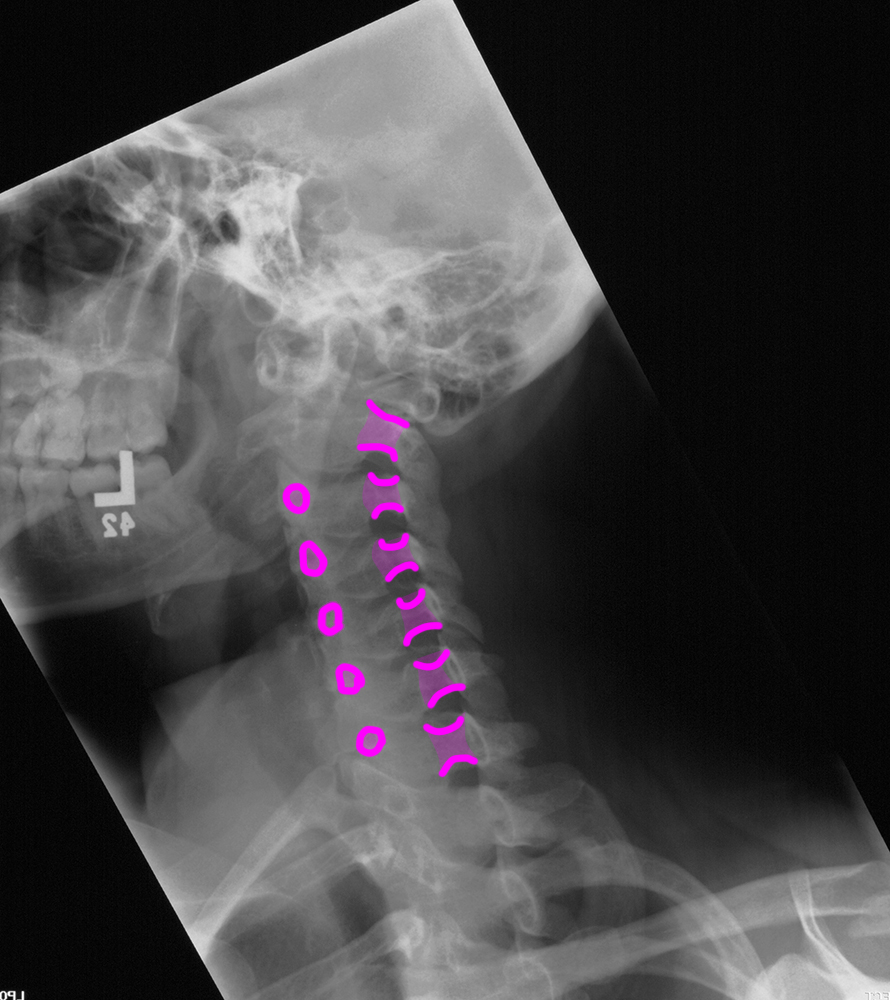
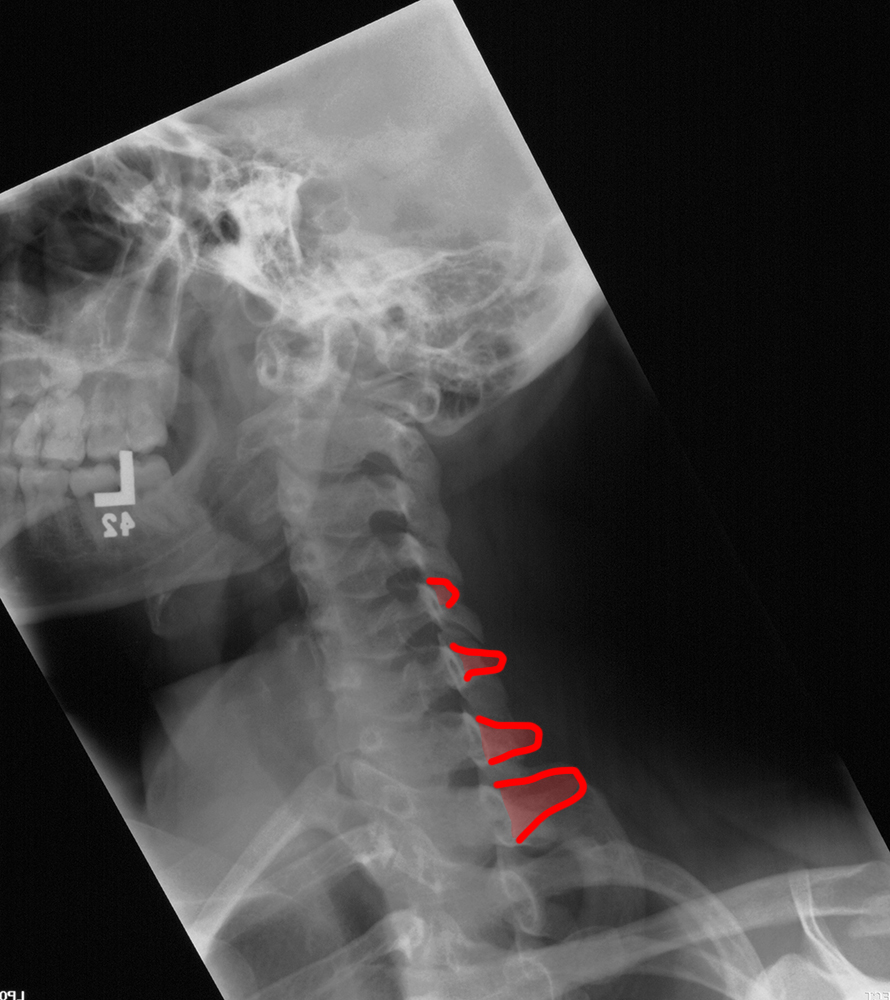
c) Use the 'clue' image below to help you identify differences between the normal image and the patient's image.
On the 'clue' image, blue dots were placed in the center of each vertebra to highlight the normal cervical spine alignment. How is this different in the patient on the left? What do you notice about the disc spaces where the red arrows are?
Case 3
This is an example of a spine radiograph in a normal patient.
Question 2:
a) What is this projection? What important structures are best seen on this view?
This is an oblique projection, and it is best for visualizing the neural foramina.
b) Identify the labeled structures below.
1-left neural foramina; 2-pedicles; 3-spinous processes 4-left laminae; 5-right transverse processes 6-left facet joints (between superior and inferior articular processes)

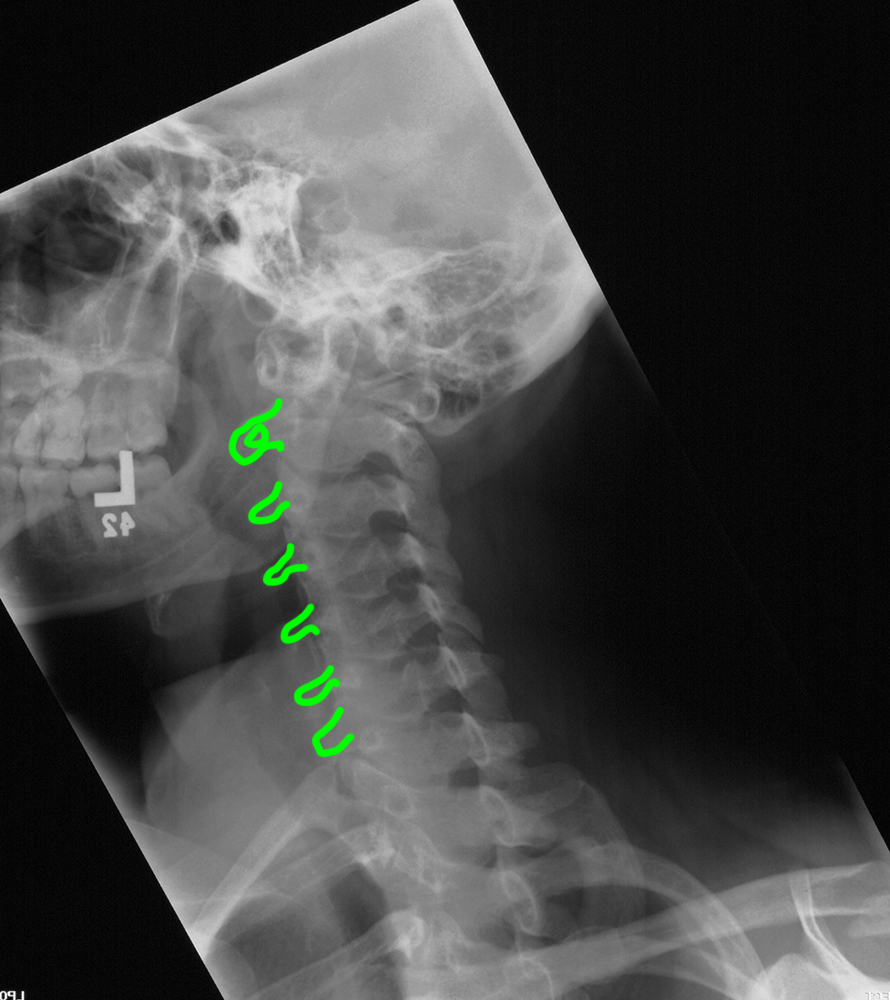
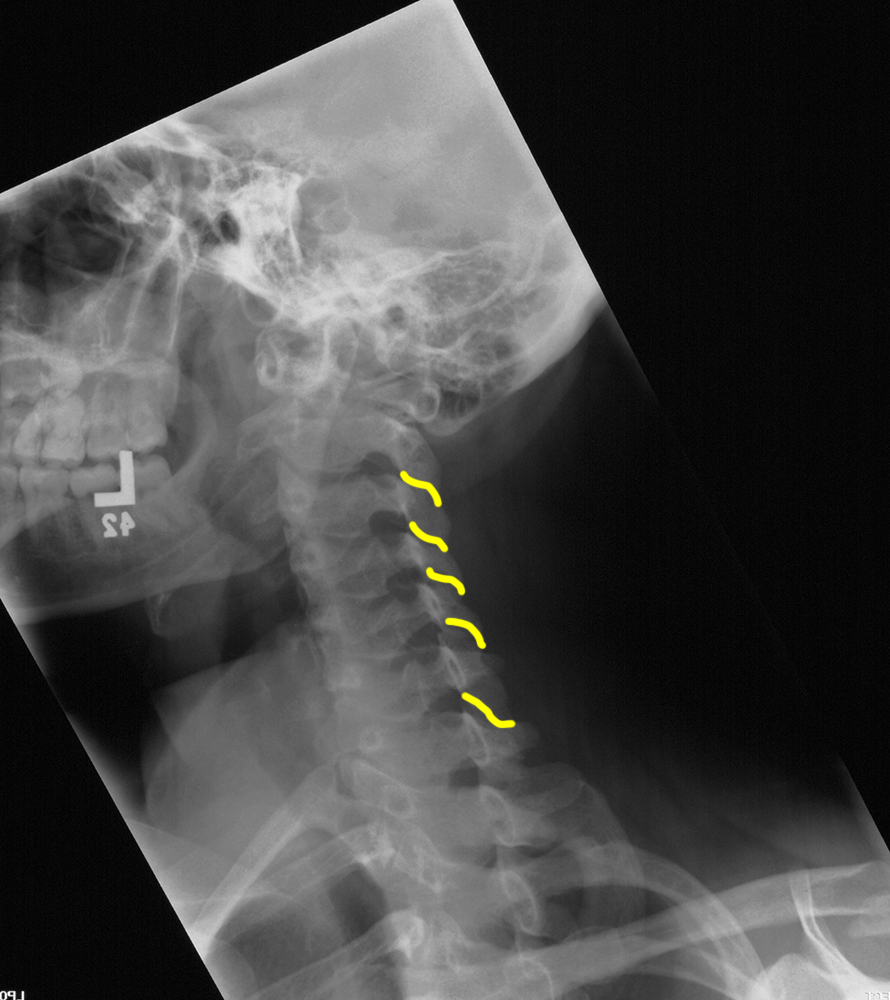
Case 3
This is also from a normal patient.
Question 3:
a) What is this view? What important anatomic structures are best seen on this view?
This is an odontoid view, also called an 'open-mouth' view. It is best for assessing the position and alignment of C1 and C2, particularly the dens or odontoid.
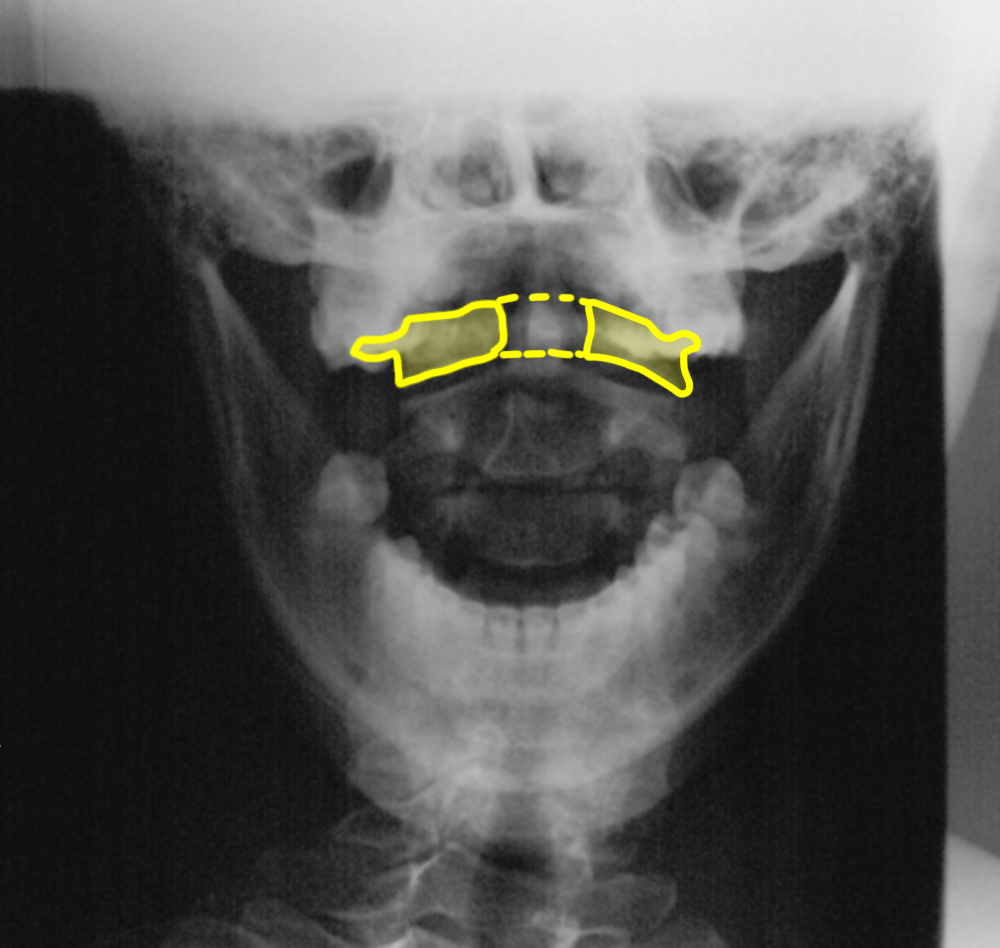
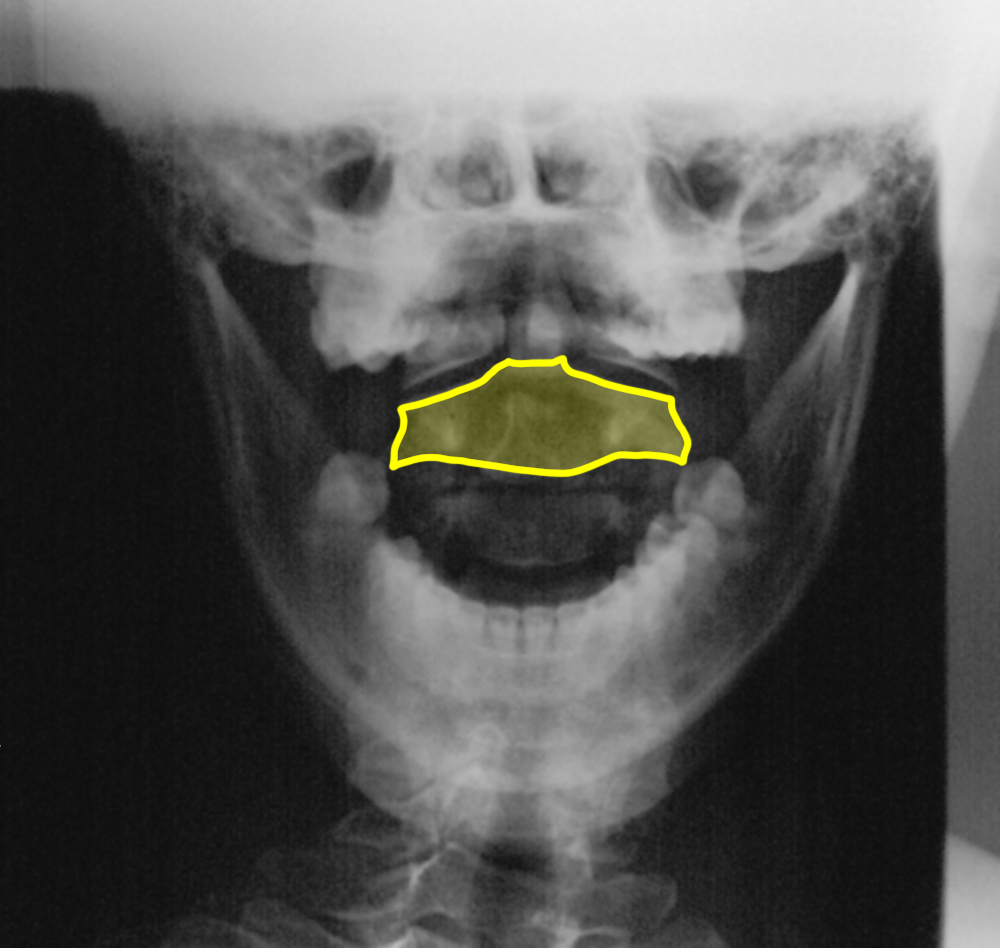
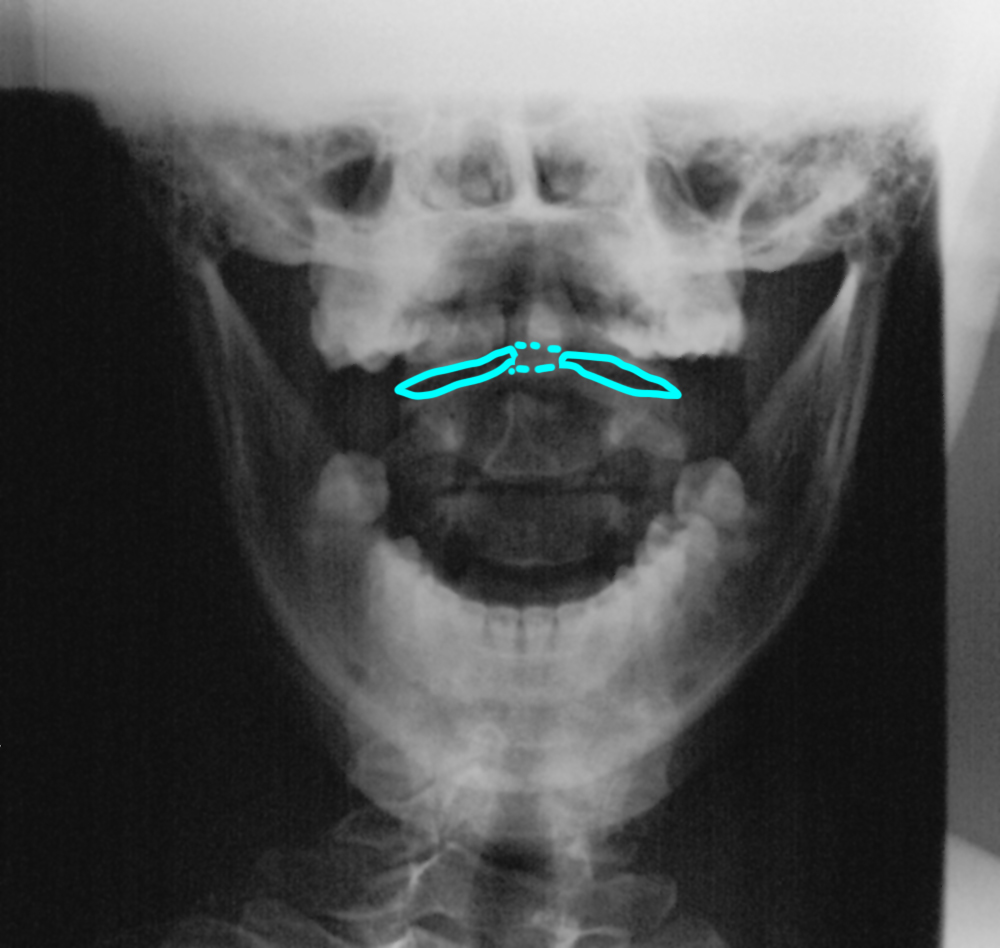
b) Identify the labeled structures.
1-dens or odontoid process; 2-body of C1 vertebra 3-body of C2 vertebra; 4-spinous process of C2 5-C1-C2 disc space
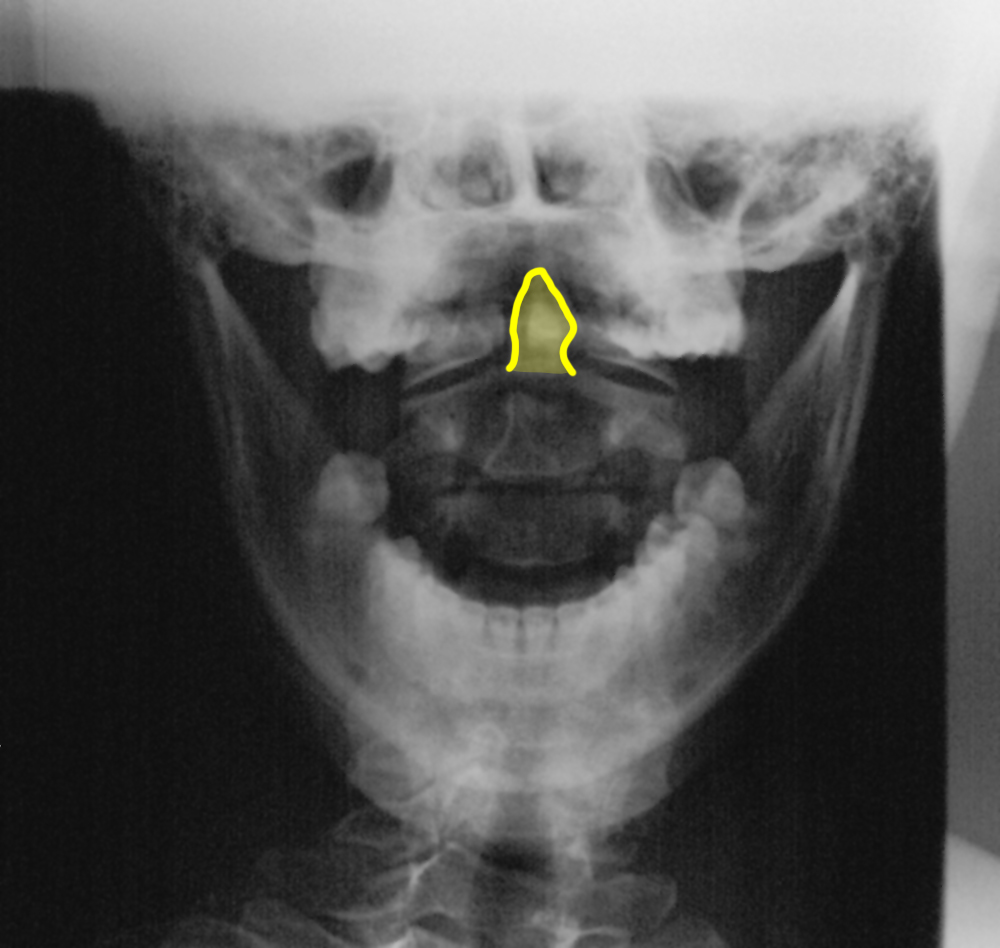
Case 3
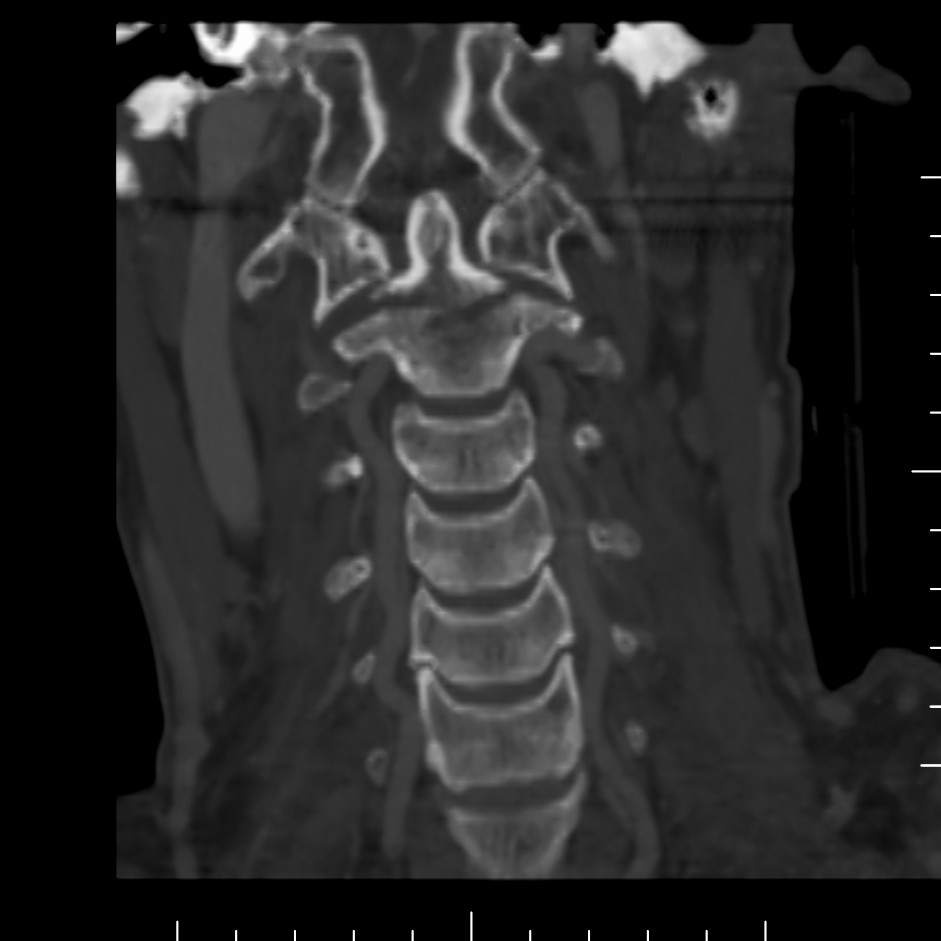
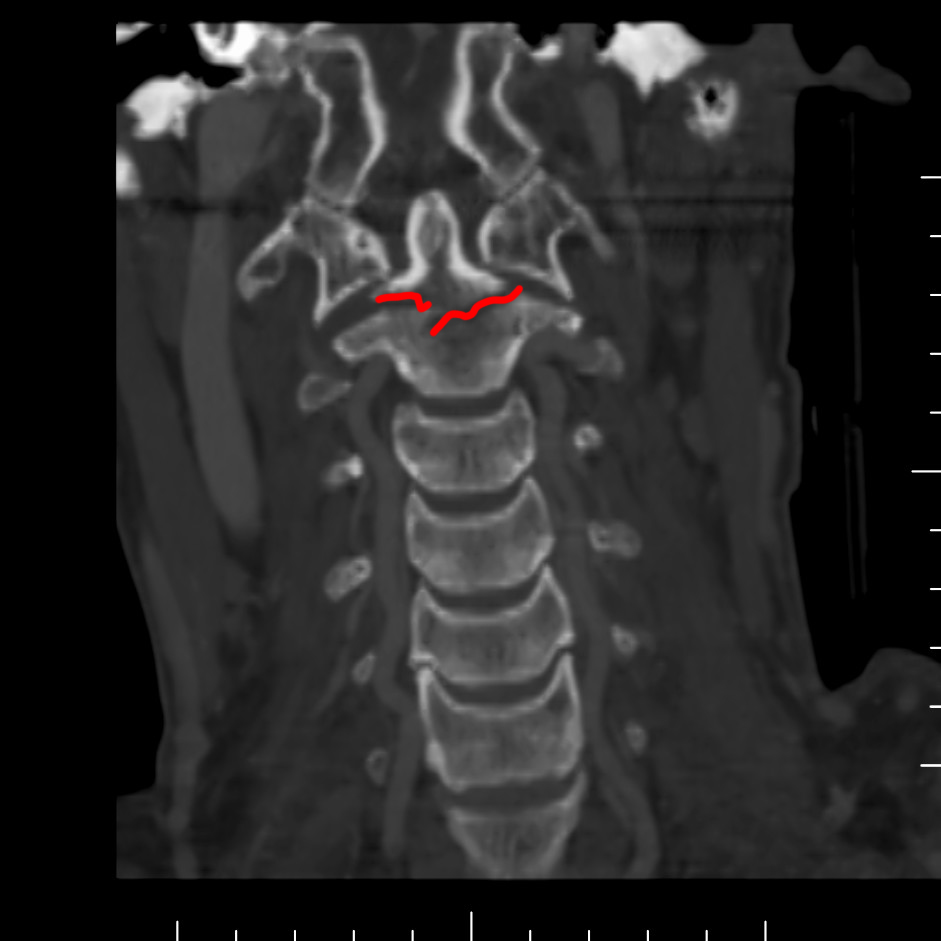
This is a study on a different patient with neck pain.
Question 4:
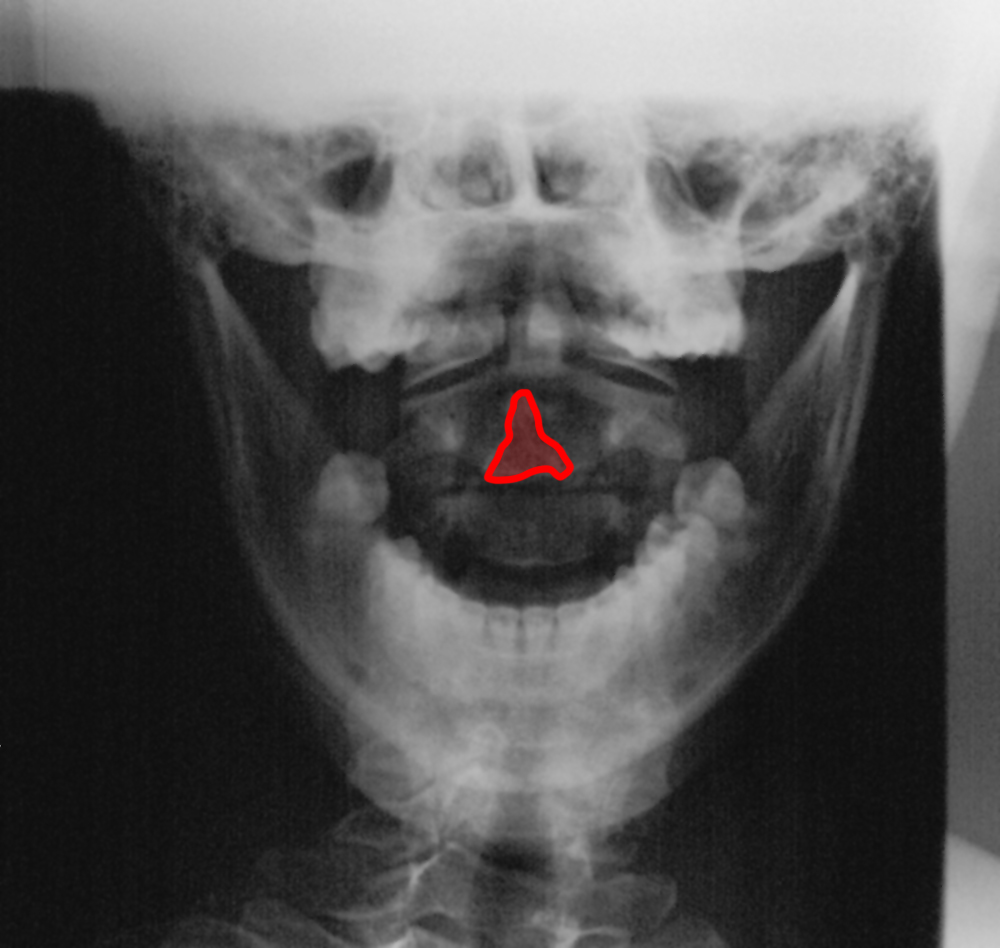
What is this study and what is abnormal?
This is a cervical spine CT scan reconstructed in the coronal plane. There is a fracture at the base of the odontoid.
Case 3
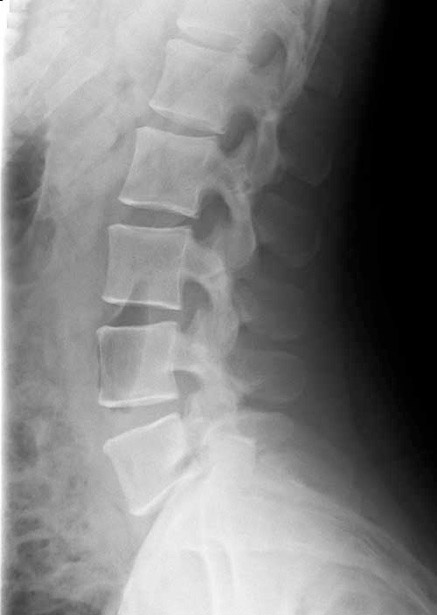
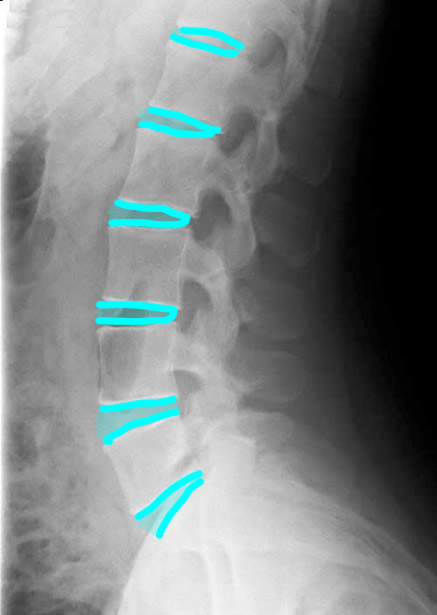
This is a study on a patient with low back pain.
Question 5:
a) What is this study and what is the projection? What abnormalities can be detected on a study of this type?
This is a lateral radiograph of the lumbar spine. This is a good survey looking for obvious abnormalities in bones, but is not sensitive for detection of soft tissue problems, such as disc herniation or ligamentous injuries.
b) Identify the labeled structures.
1-lumbar disc spaces; 2-pedicles; 3-superior articular facets 4-inferior articular facets; 5-spinous processes; 6-neural foramina
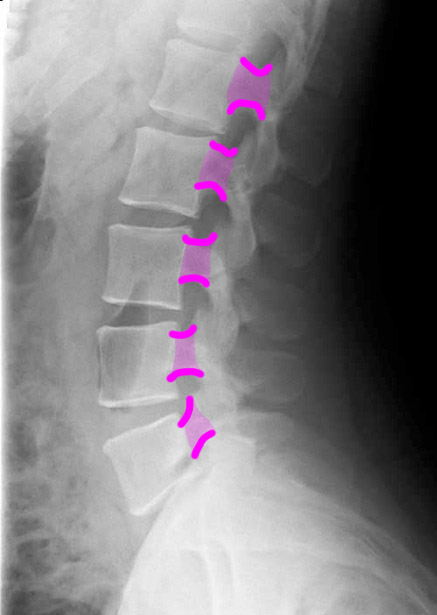
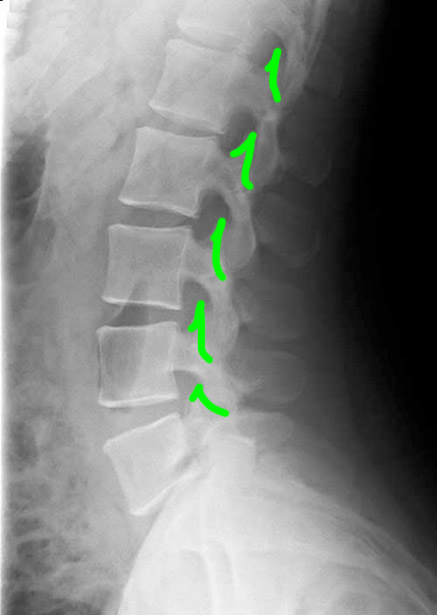
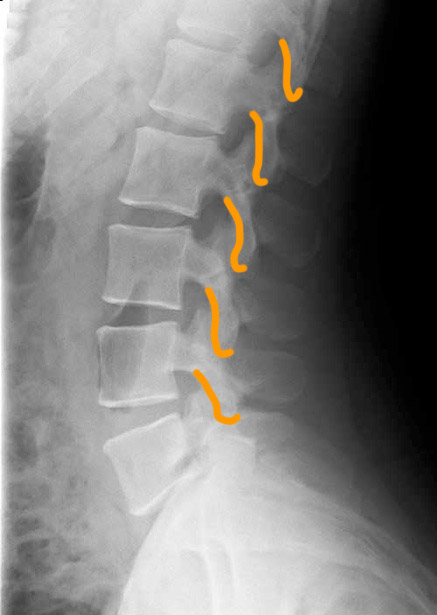
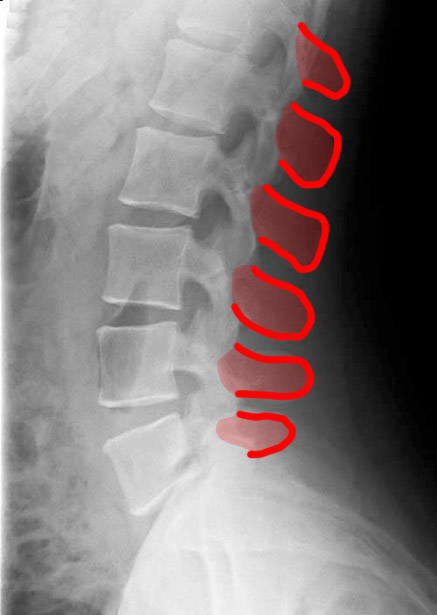
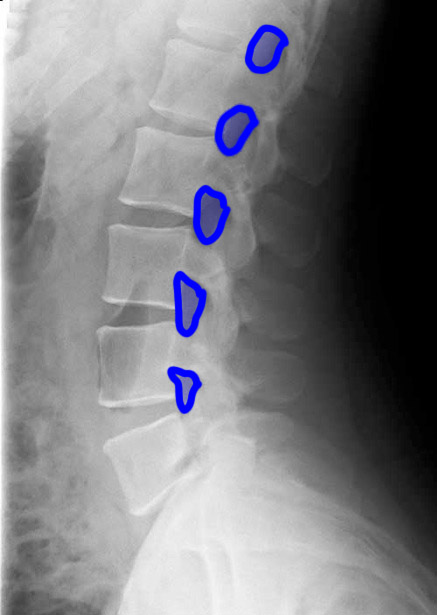
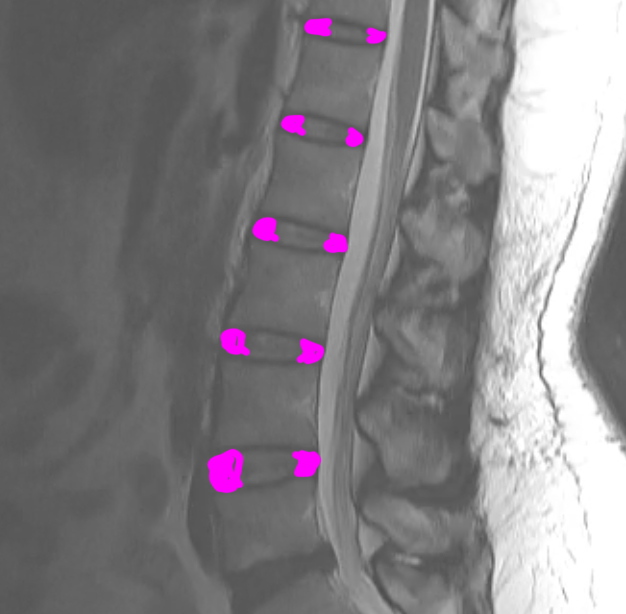
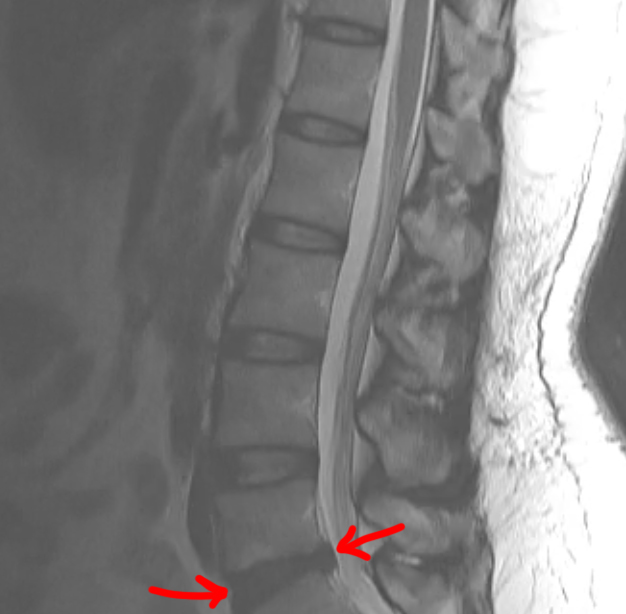
Case 3
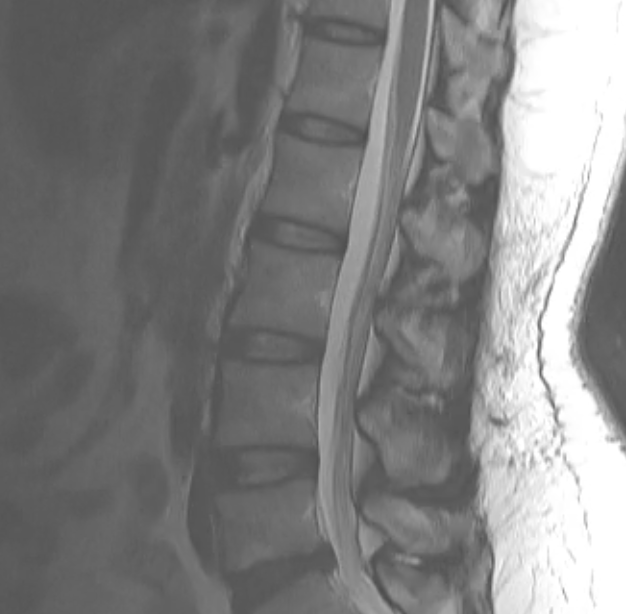
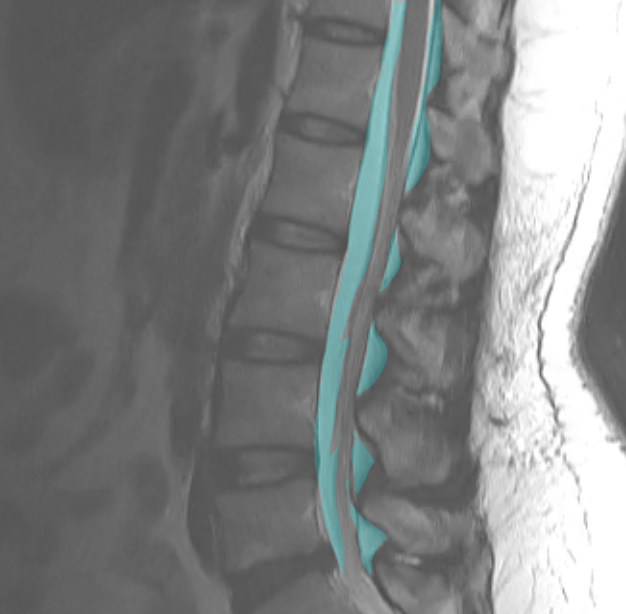
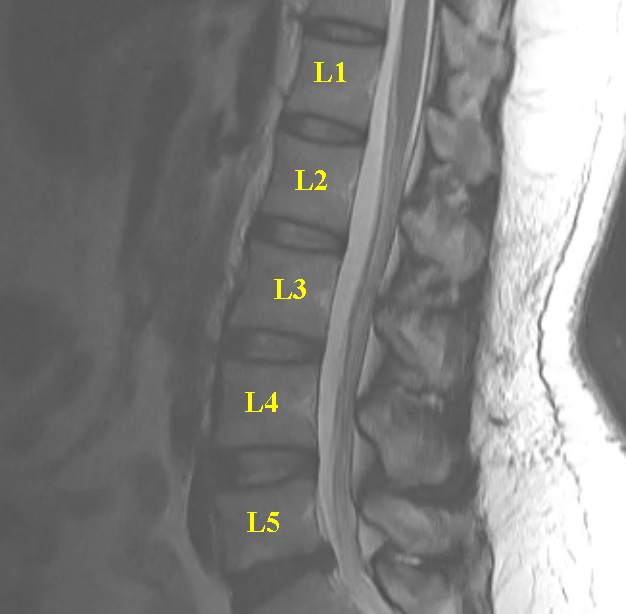
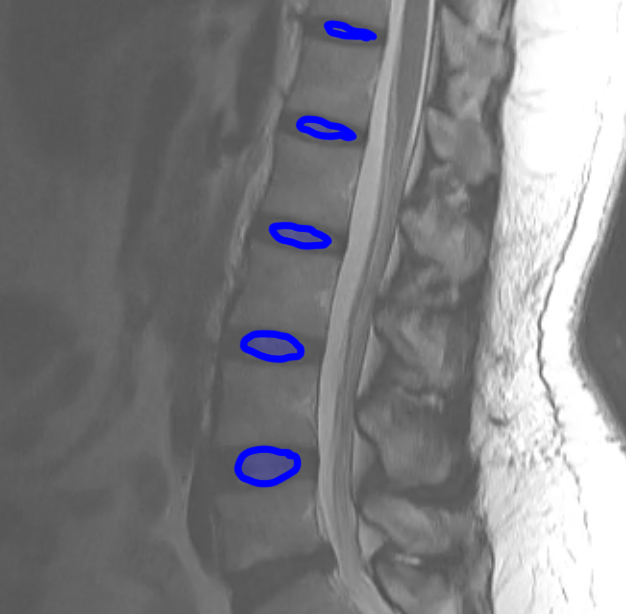
This study is from a different patient, also with low back pain. Use the links to bring up different findings on the image.
Question 6:
What is this study, and what are important technical parameters to note? What types of abnormalities are best seen in a study of this type?
This is a T2-weighted MR in the sagittal plane. This type of study is good for detecting soft tissue abnormalities, such as abnormal discs or ligamentous abnormalities. Unfortunately, imaging findings and clinical symptoms may not always match, so patients may have significant complaints without imaging findings. or may have obvious imaging findings without complaints referable to the involved level.