








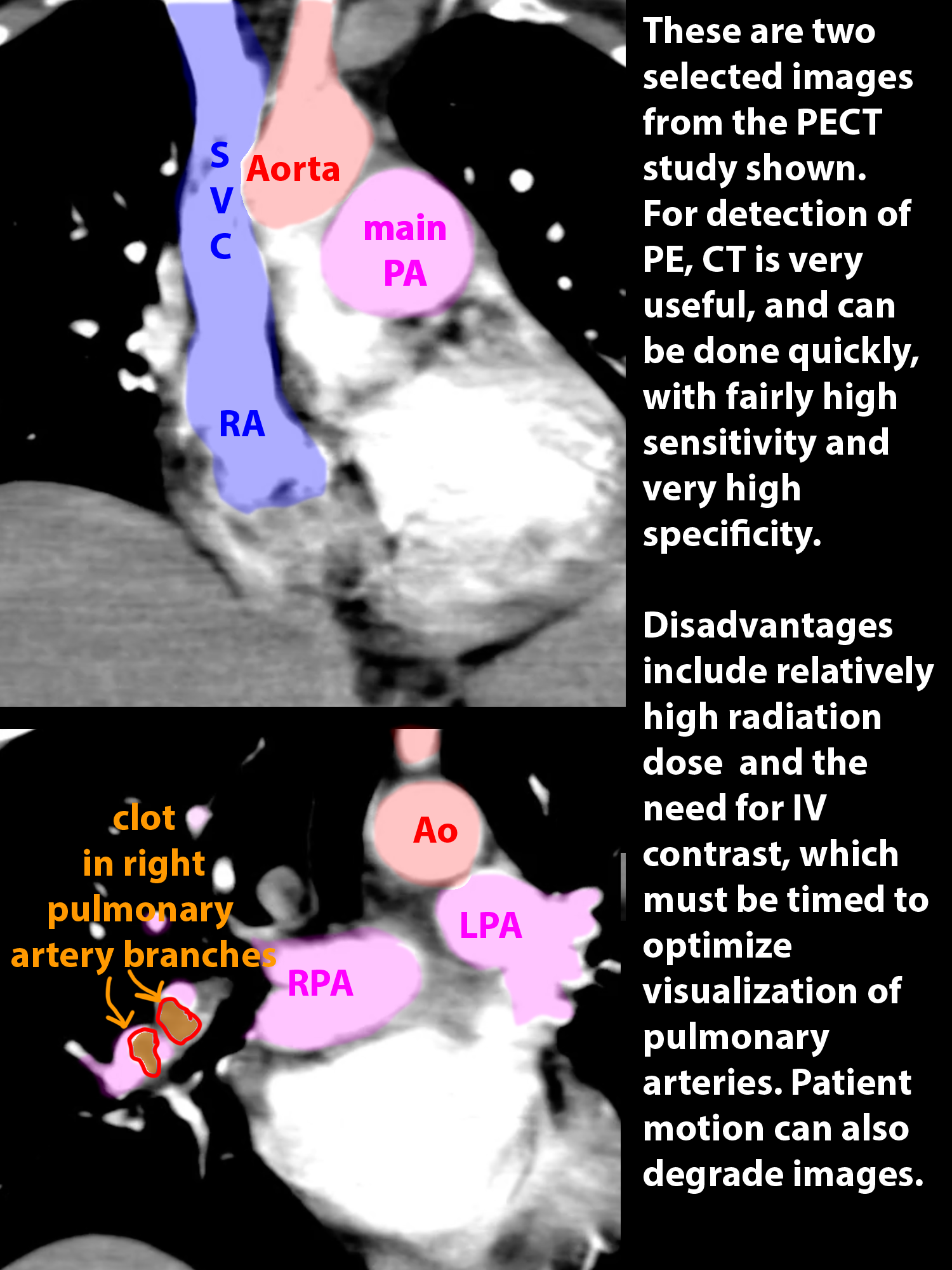
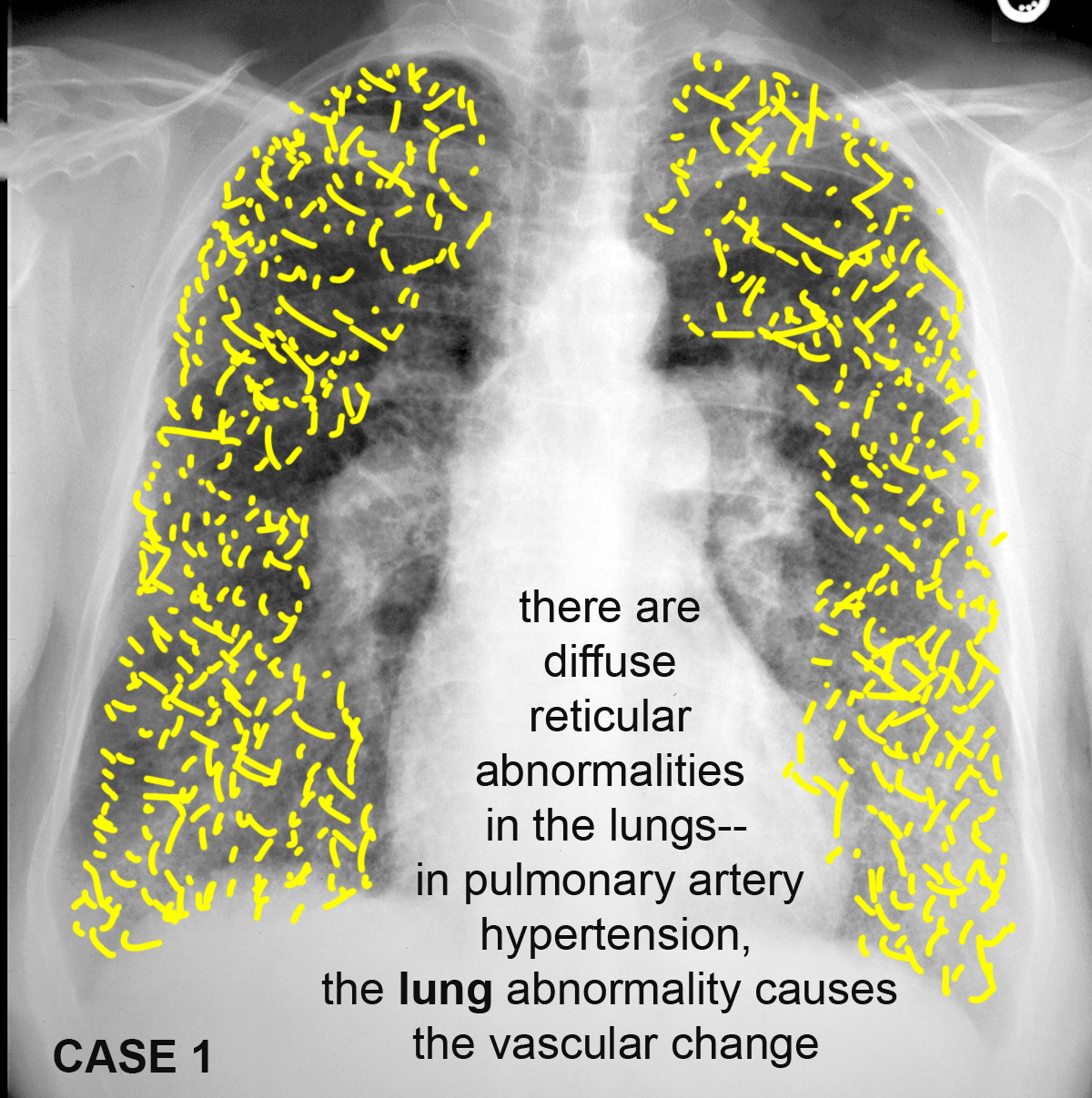
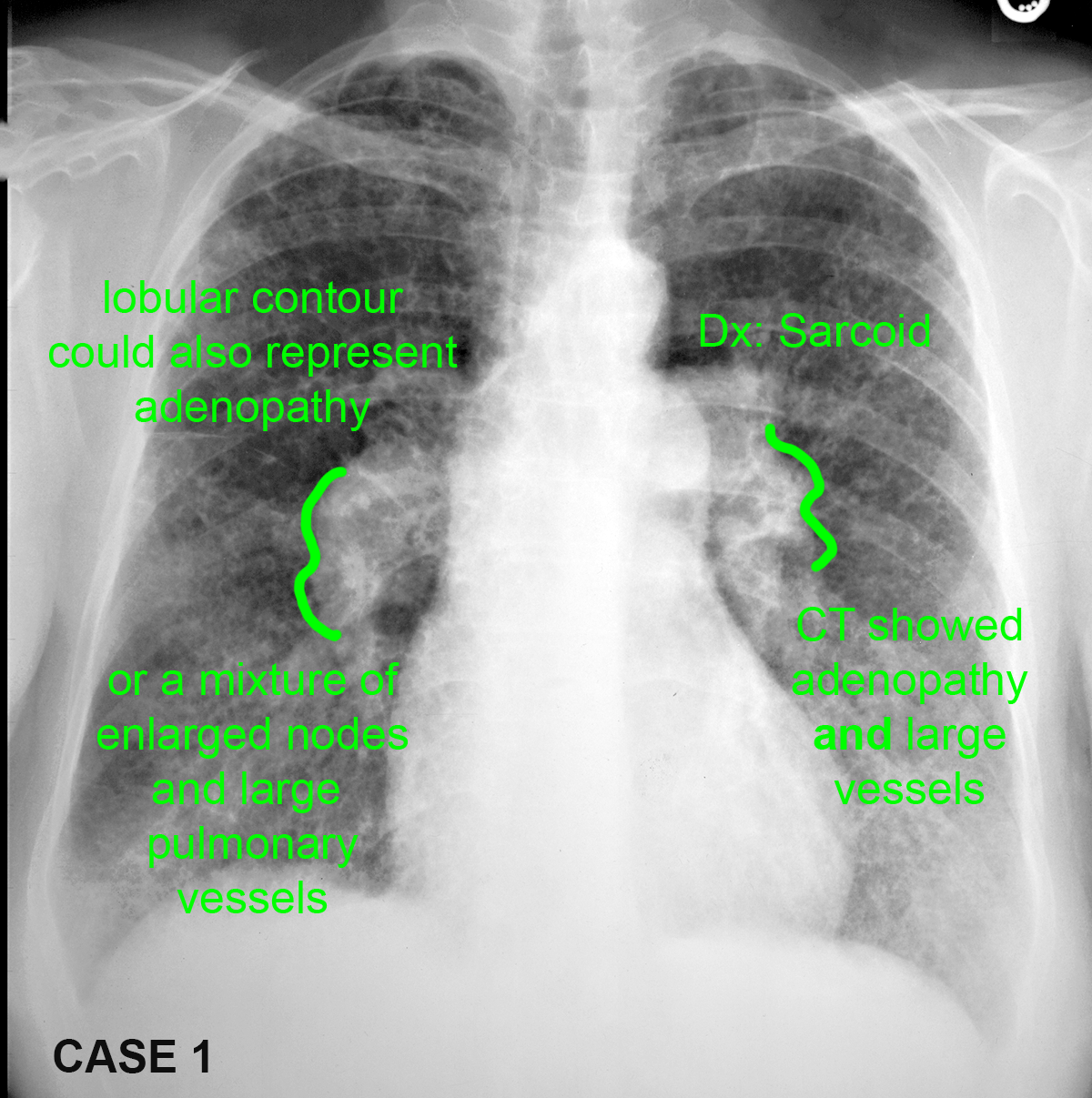
Case 3--pulmonary vascular disease
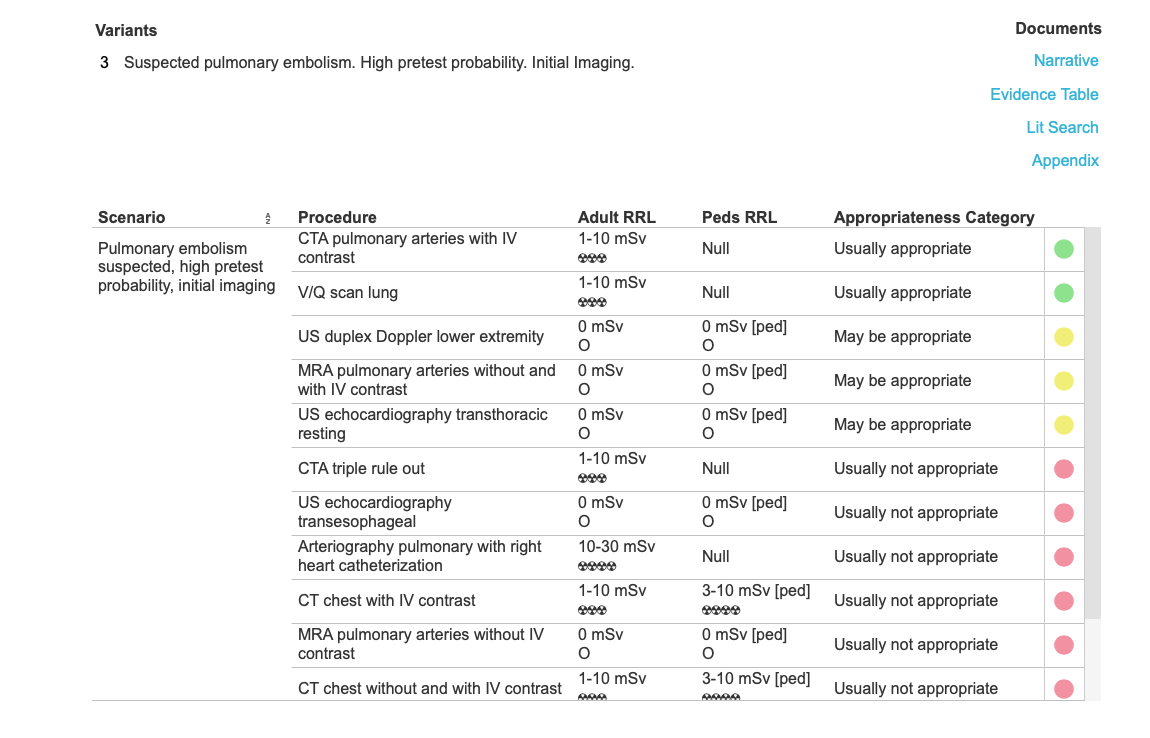
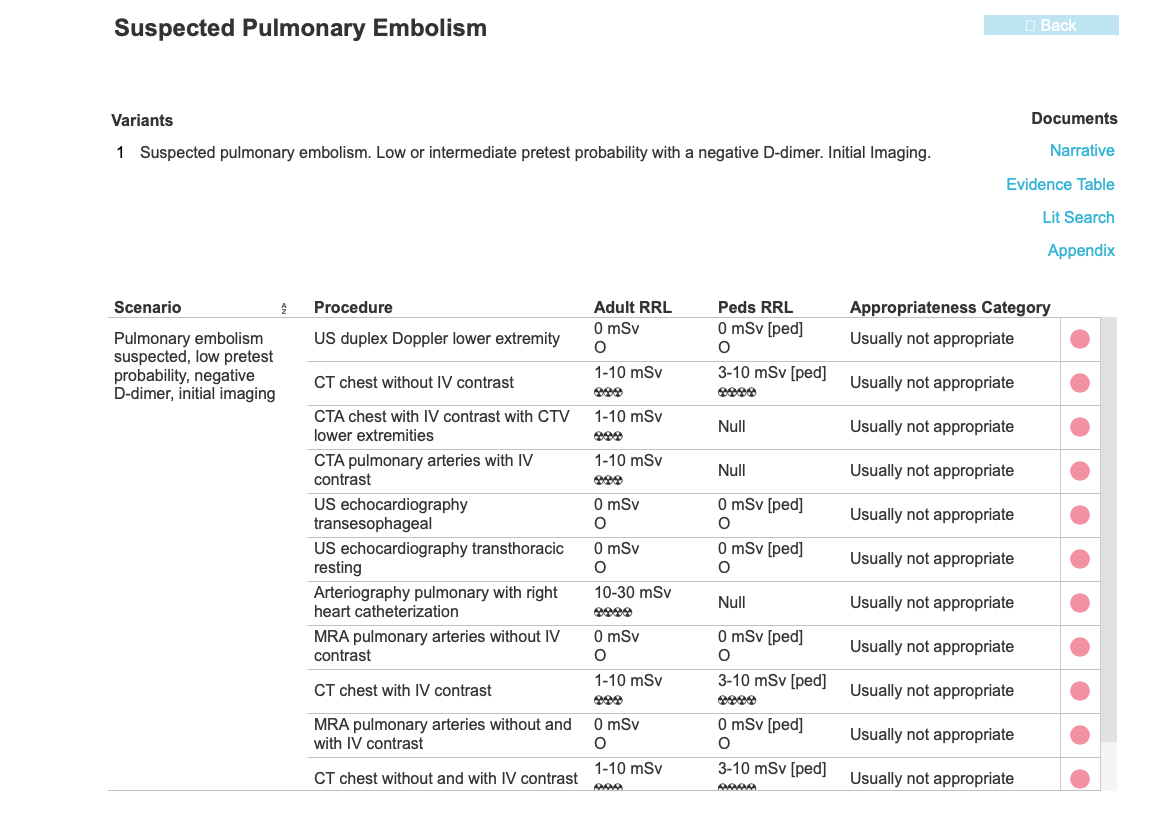
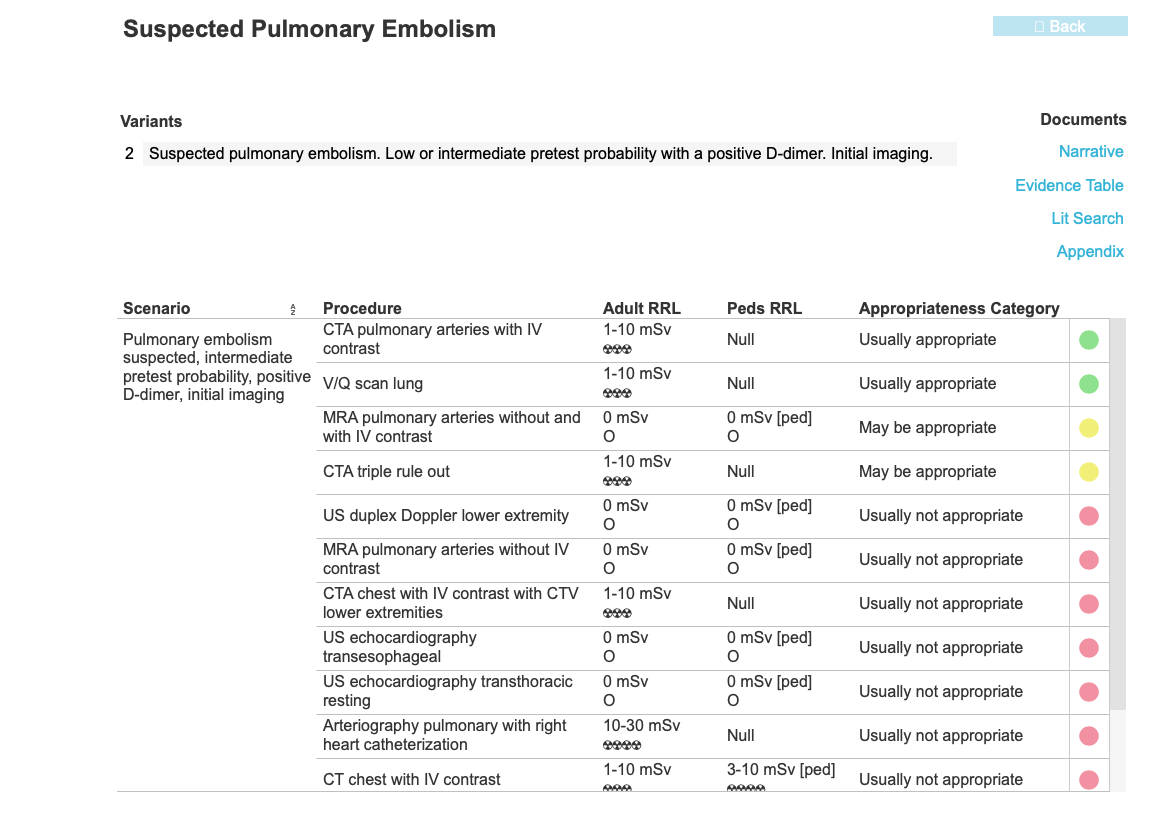
This page addresses a common condition involving the pulmonary vasculature, pulmonary embolism. The symptoms of this condition are somewhat nonspecific and include shortness of breath and chest pain. Lab tests can be helpful, particularly D-dimer, which can indicate the presence of intravascular clot, but not where it is located. To determine whether clot is present in the pulmonary vasculature, imaging often plays a large role.
Further Explanation:
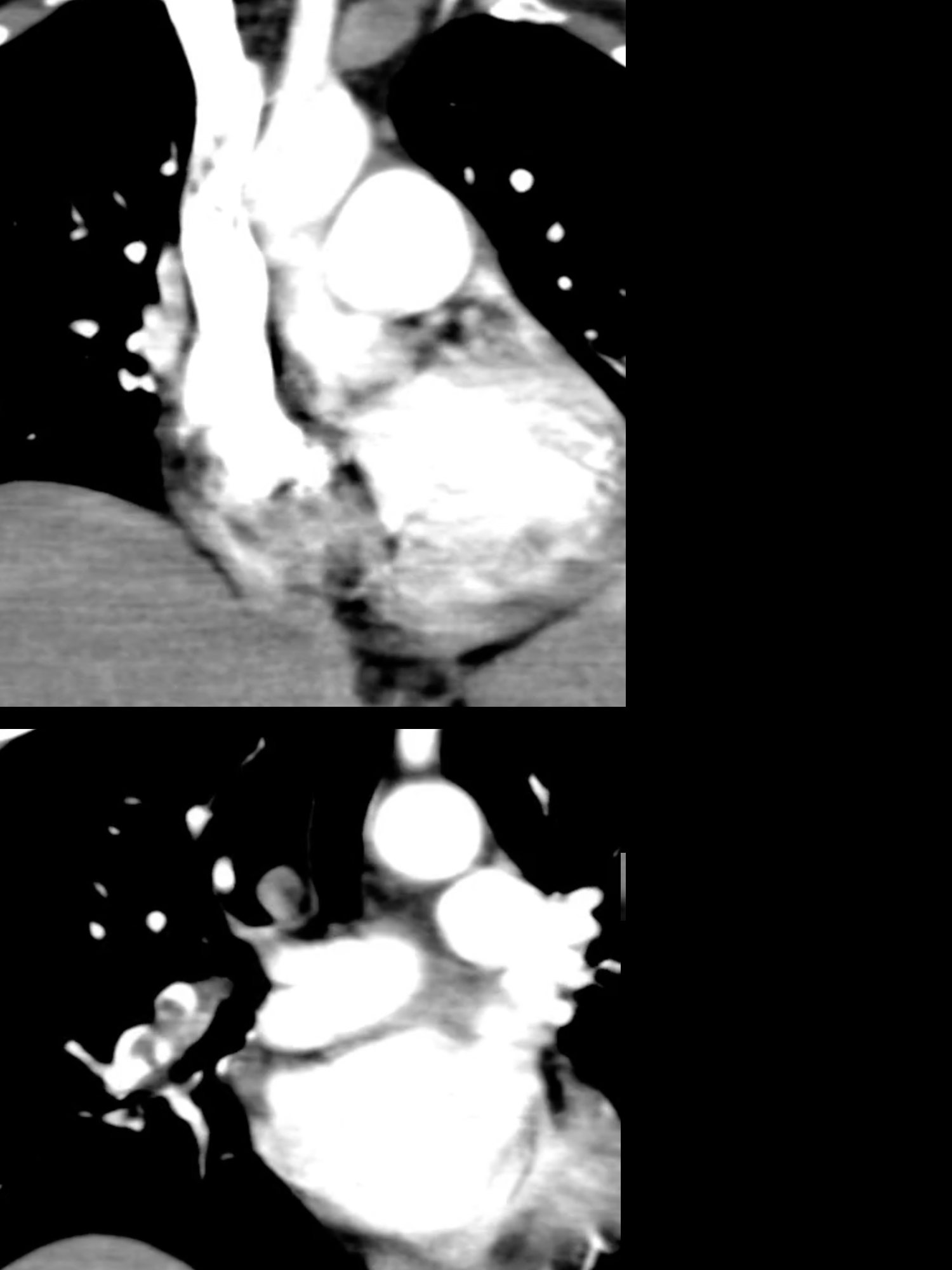
Case 3--pulmonary vascular disease
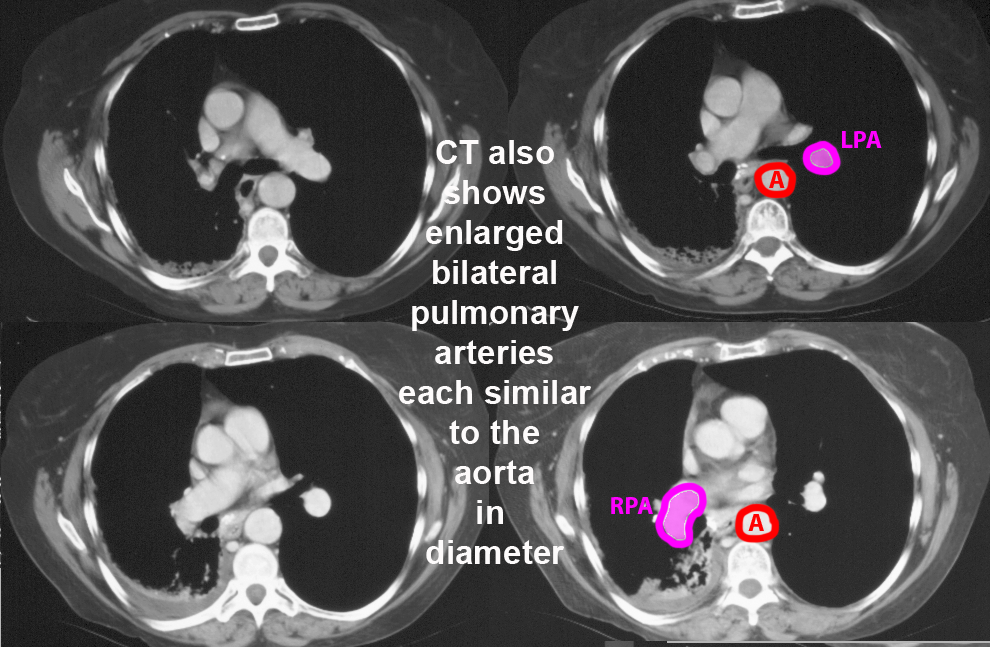
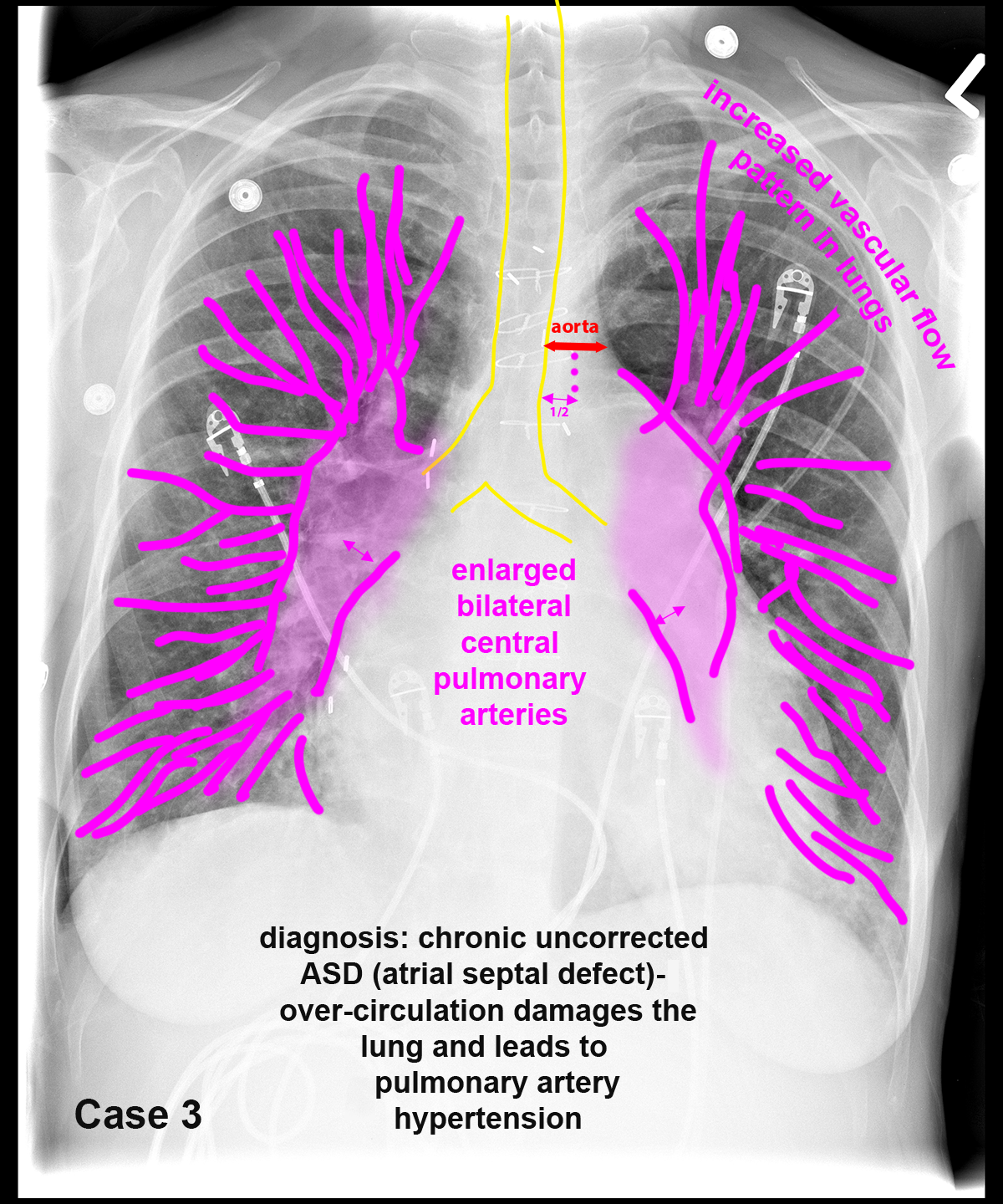
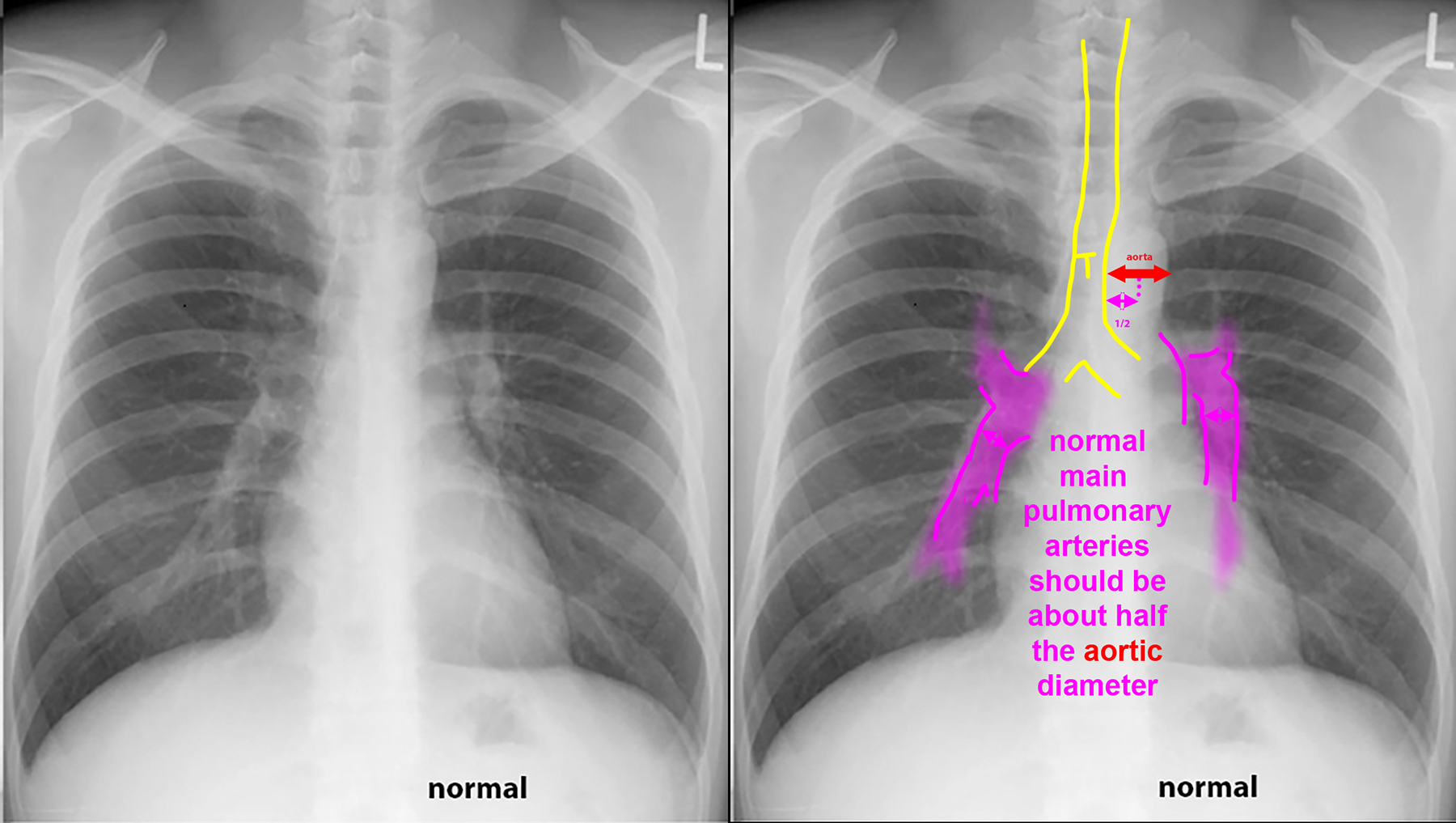
These patients all have abnormal pulmonary arteries on imaging. Decide how you would describe the imaging findings. How can you tell if a main pulmonary artery (in the hilar region) is enlarged?
Further Explanation:
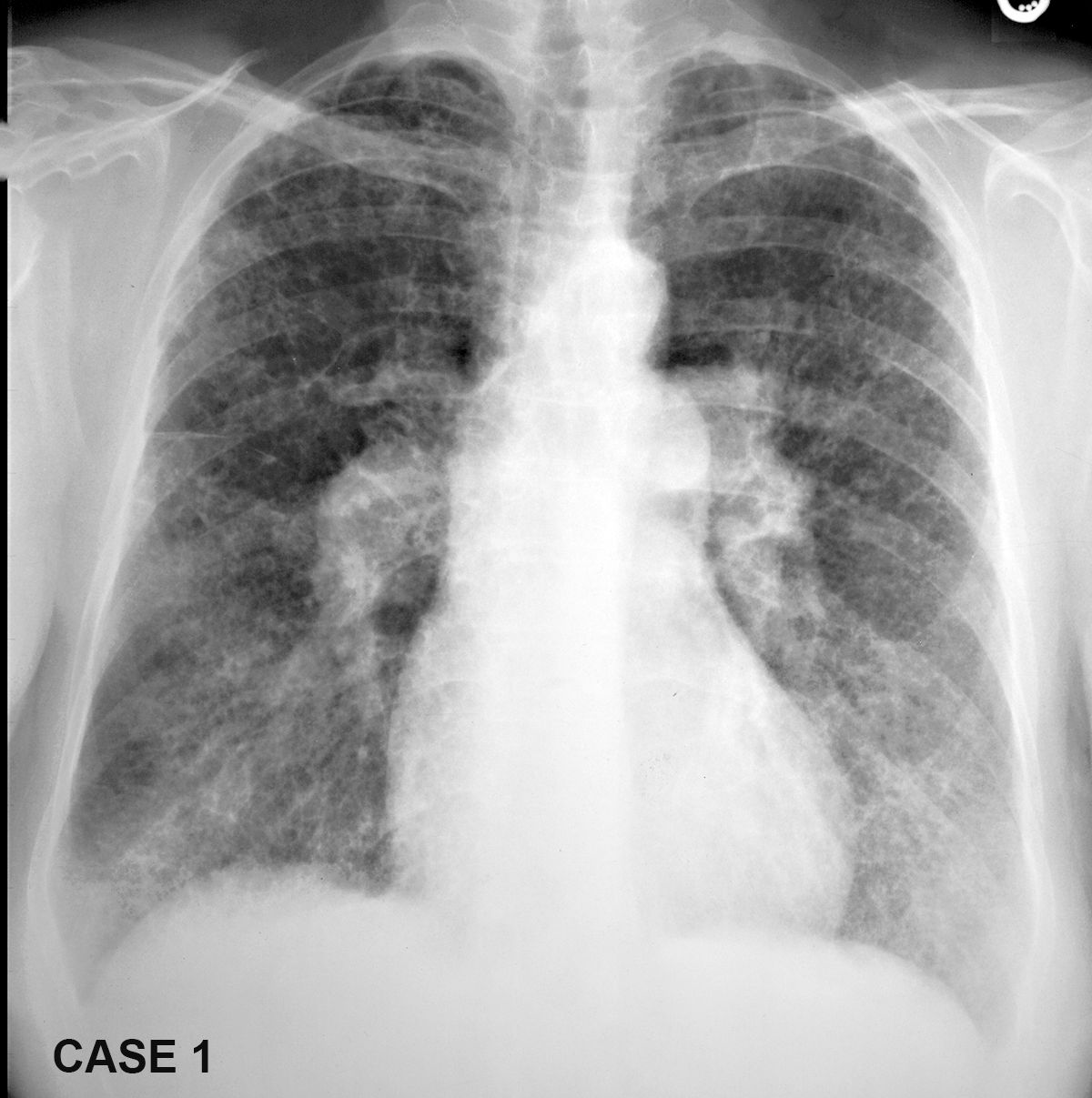
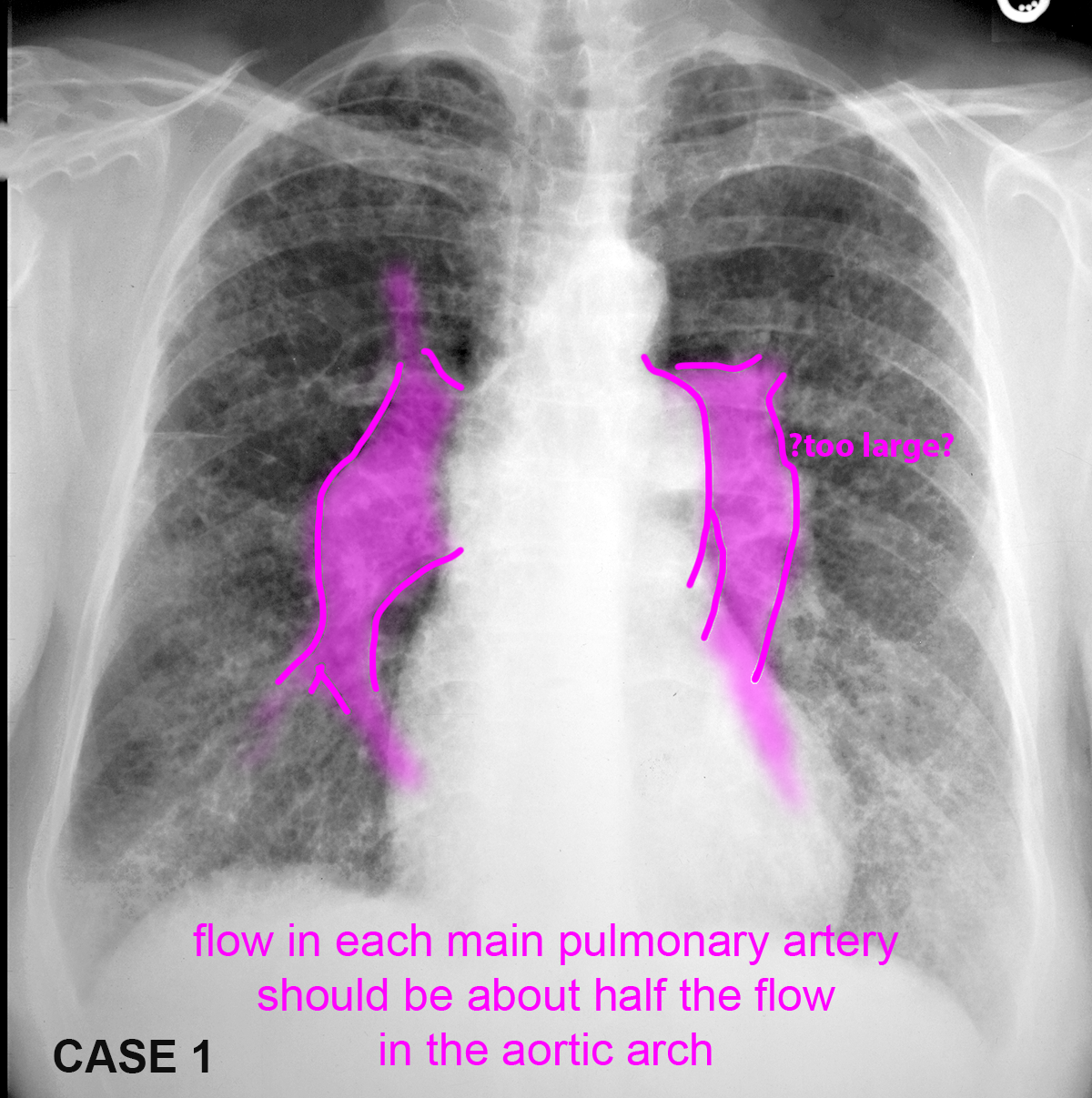
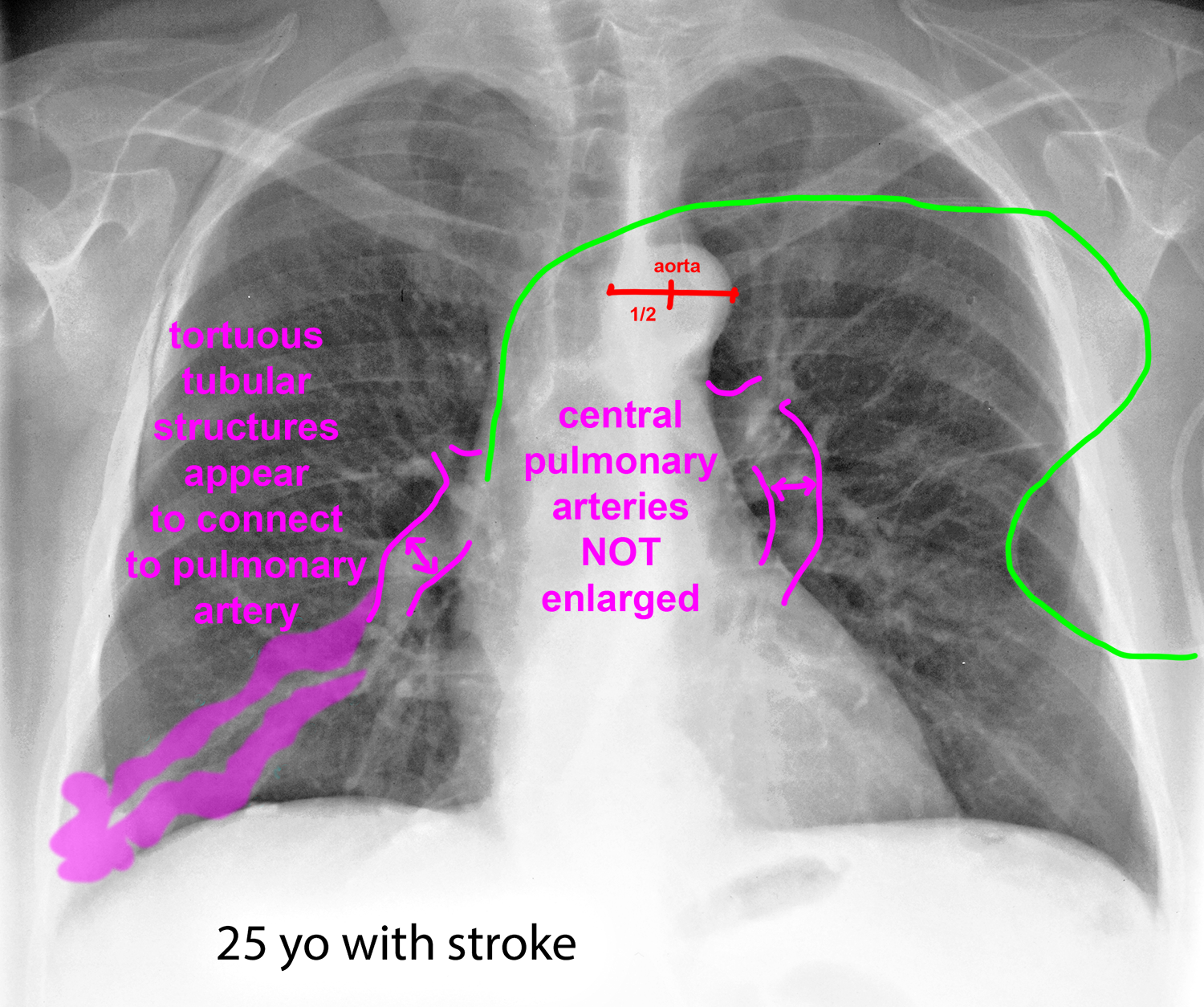
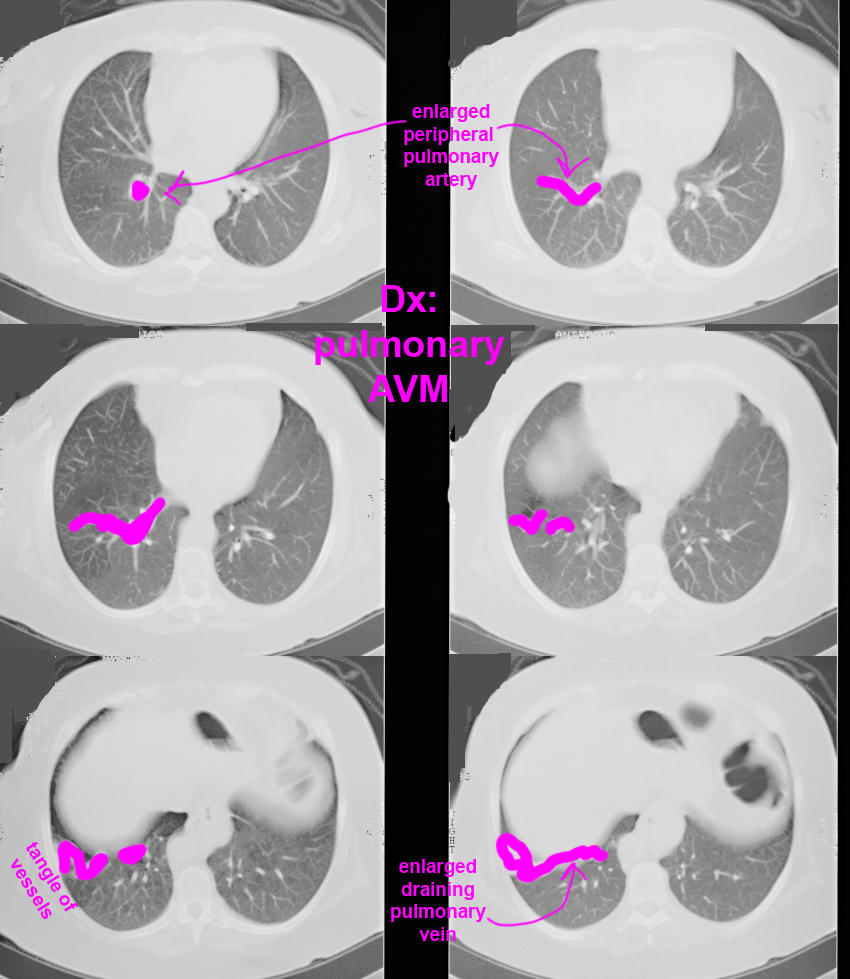
Case 3--pulmonary vascular disease
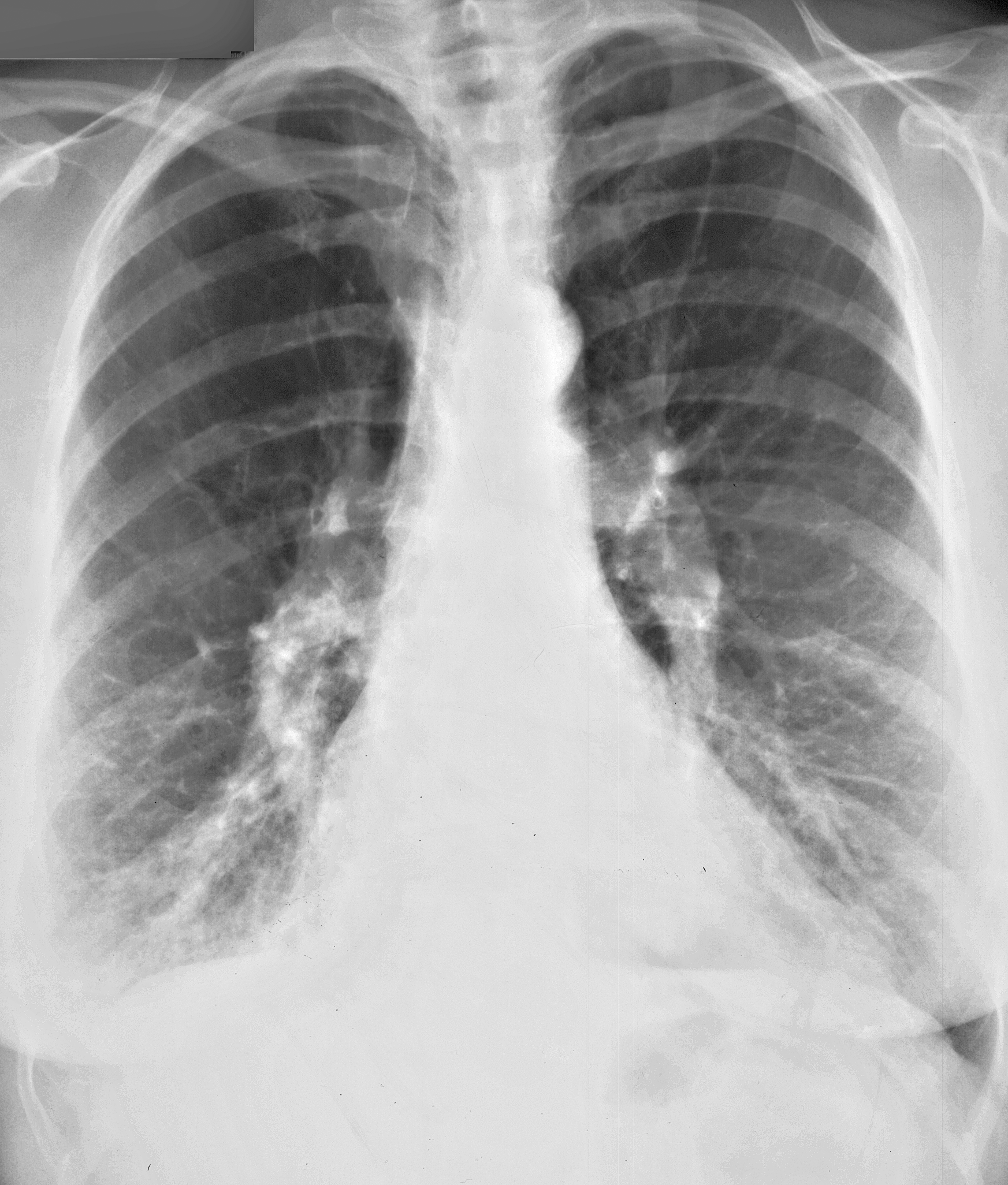
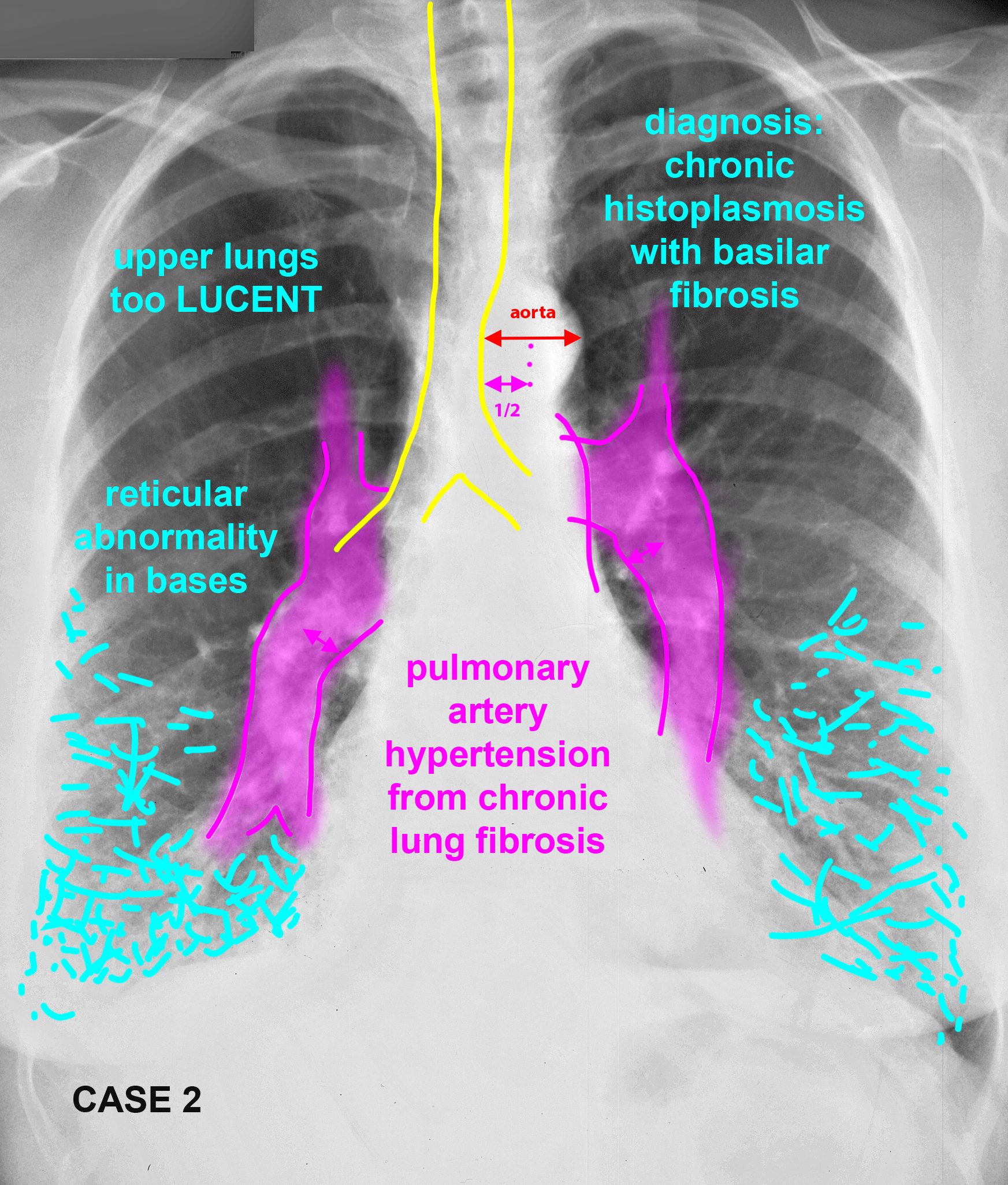
This patient also has a vascular abnormality. How does the location of the finding help you in deciding what it is likely to be?
Further Explanation: